2021 - III Quarterly Bulletin
NC3 TOP – Threat Observatory Platform
Threat Agent activities
Behind every cyber-attack there is an actor with a specific intent. However, for many events, the identity and general motivation are unknown. On the other hand, some groups have been well known for years and their criminal activities and techniques are documented and monitored. Typically, they conduct targeted attacks against specific organisations, using relatively sophisticated tools and attack procedures.
Some of them are considered as State-sponsored, but the actual link with various countries stays often subject of controversies and should be considered with prudence.
As during previous quarters, the attribution rate of events is very low. This means that most of the ongoing attacks are not attributable.
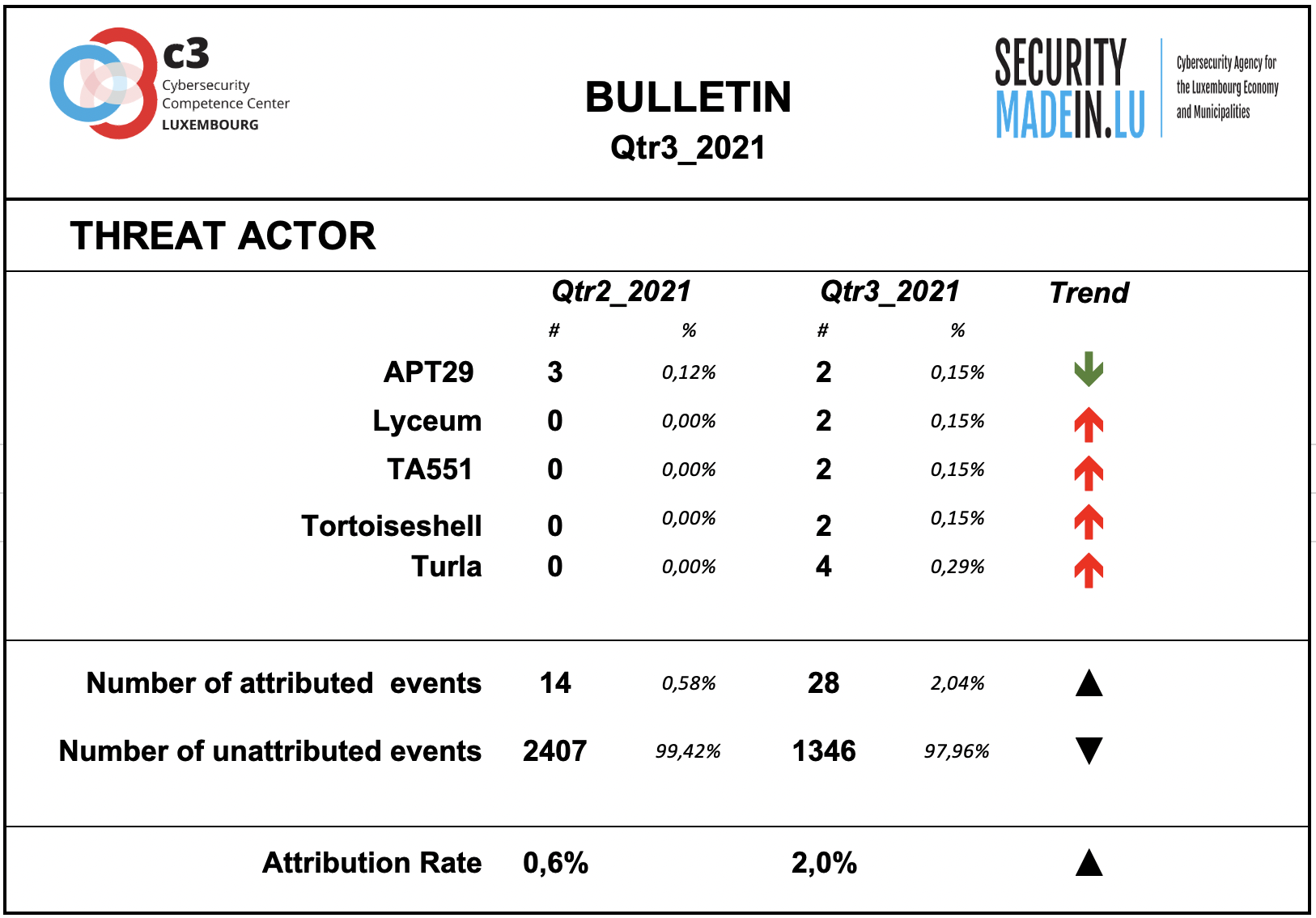
According to the attribution found in the MISP records, the following groups were particularly active during this quarter:
APT29 is a Russian hacker group believed to be associated with one or more intelligence agencies of Russia; it primarily targets Western governments and related organizations, such as government ministries and agencies, political think tanks, and governmental subcontractors;
Lyceum is an emerging threat to energy organizations in the Middle East, but it should not assume that future targeting will be limited to this sector. Lyceum 's targeting of telecommunications has been speculated to be part of an effort to establish man-in-the-middle capabilities throughout the Middle East region;
TA551 is a financially-motivated threat group that has been active since at least 2018. The group has primarily targeted English, German, Italian, and Japanese speakers through email-based malware distribution campaigns;
Tortoiseshell this has been active since at least July 2018. Symantec has identified a total of 11 organizations hit by the group, the majority of which are based in Saudi Arabia. In at least two organizations, evidence suggests that the attackers gained domain admin-level access;
Turla this group specialised in espionage activities and intelligence gathering motivations, targeting organizations worldwide. It is considered as emanating from Russia.
External transfer pathway and infrastructures
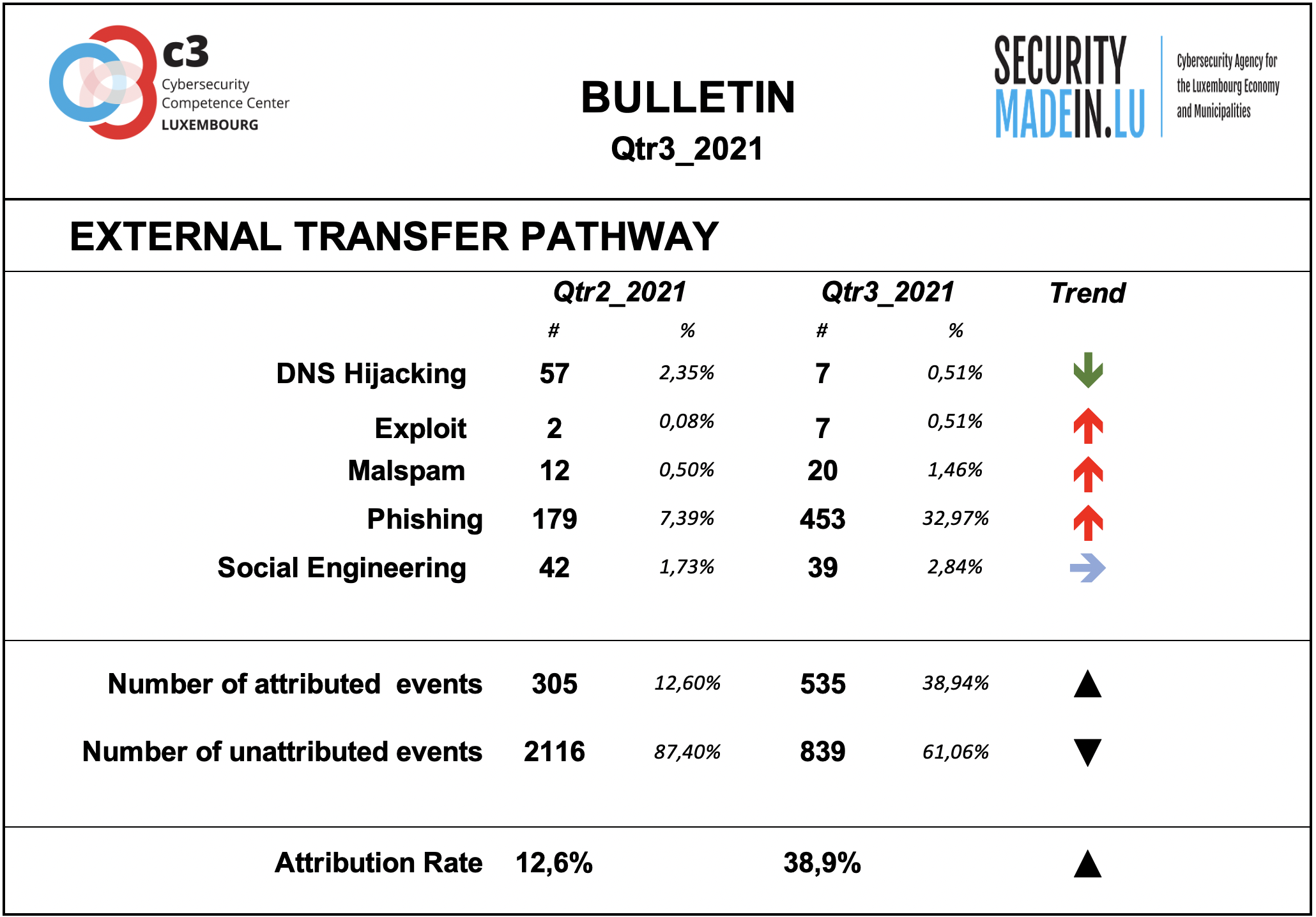
The transfer of the malicious artefacts or payloads is done through a number of different types of technical procedures and infrastructures.
Also, during this quarter of 2021, it is confirmed that the most frequently used strategy is associated with scams that use email or similar approaches to reach potential victims. The data collected show a significant increase of phishing events. Phishing is the most common strategy, but there has also been an increase in malspam and smishing events. In most of these cases, the pathway is a human to human or machine to human infrastructure.
The attribution rates are significantly better than for threat actors. Attribution means that it was possible to identify the external transfer pathway for a given event.
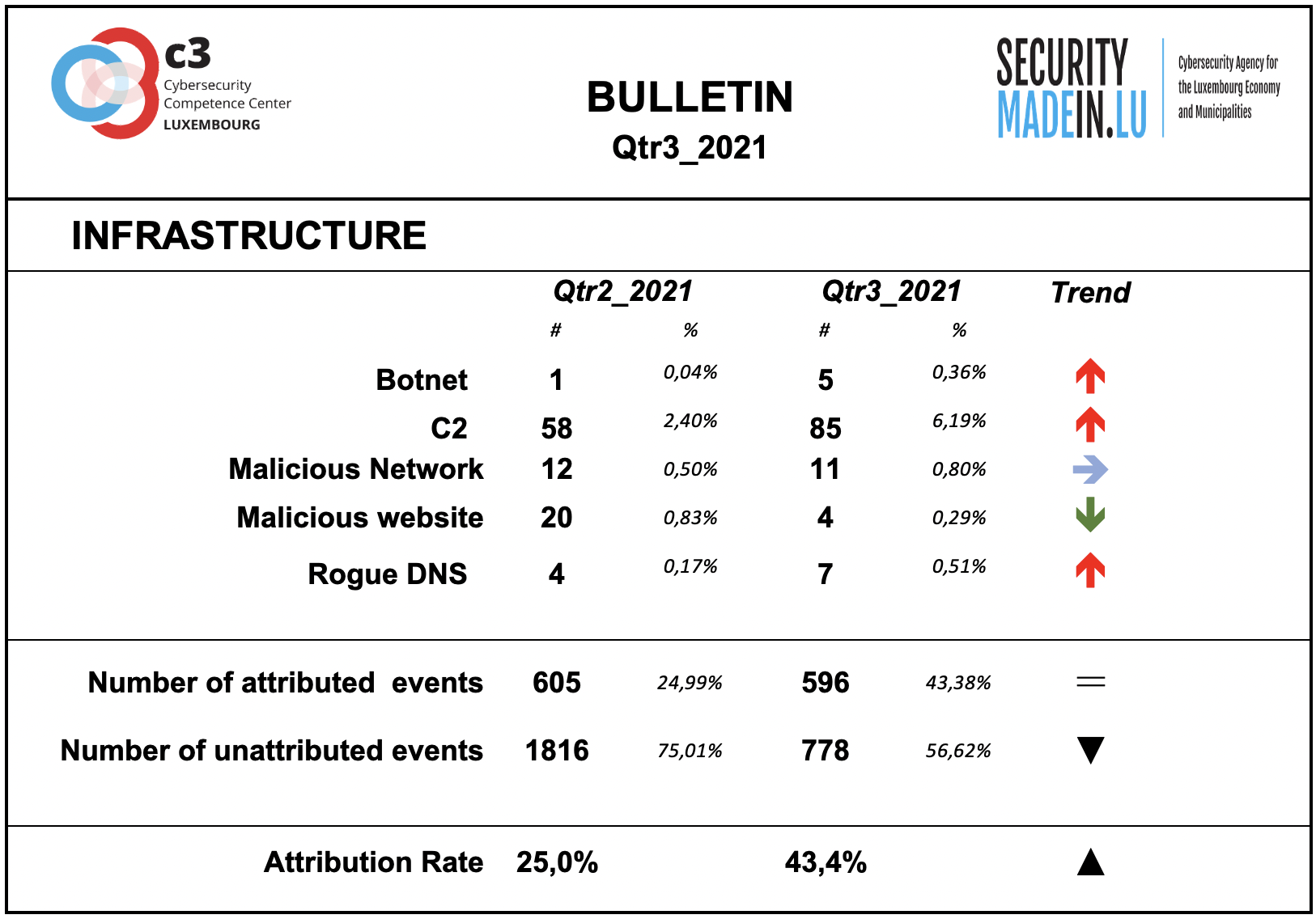
Infrastructures represent the type of systems being used for supporting attacks. Some are meant to compromise or help compromise, the targeted system, others are more focused on helping to maintain the foothold in it. Indeed, once access to a system device has been gained, a communication channel is maintained through the use of command and control (C2) infrastructures. The specific mechanisms vary greatly between attacks, but C2 generally consists of one or more covert communication channels between devices in a victim organization and a platform that the attacker controls. These communication channels are supporting the malicious activities. They are used to issue instructions to the compromised devices, download additional malicious payloads, and pipe stolen data back to the cyber-actor.
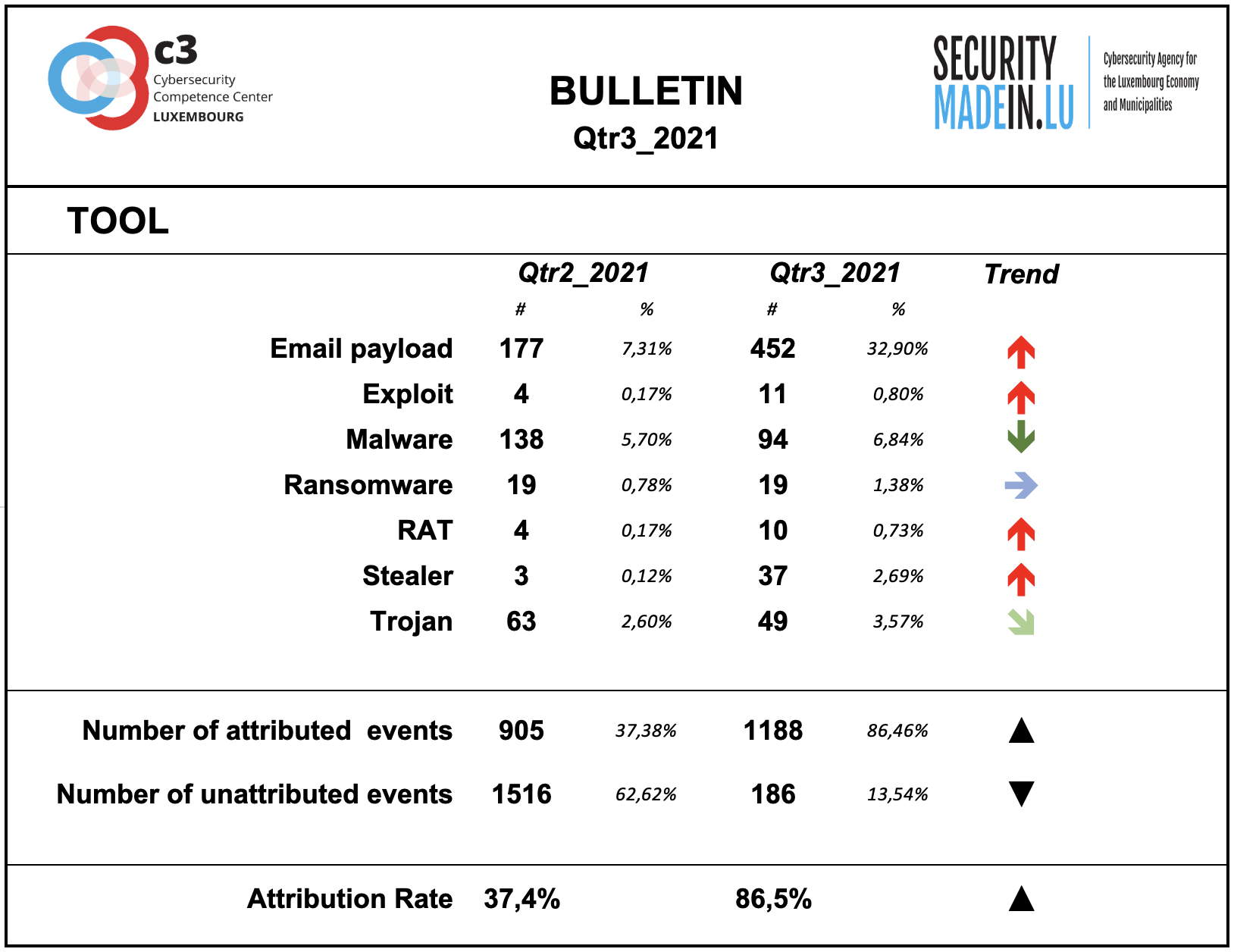
Tool
The monitoring system showed a substantial prevalence of the use of Malware especially associated with IoT systems.
During this quarter, ransomware tool are still in evidence.
The data collected show a significant increase in the use of stealing tools.
Compared to the other dimensions of the interpretation model, this dimension is confirmed as having the highest attribution rate.
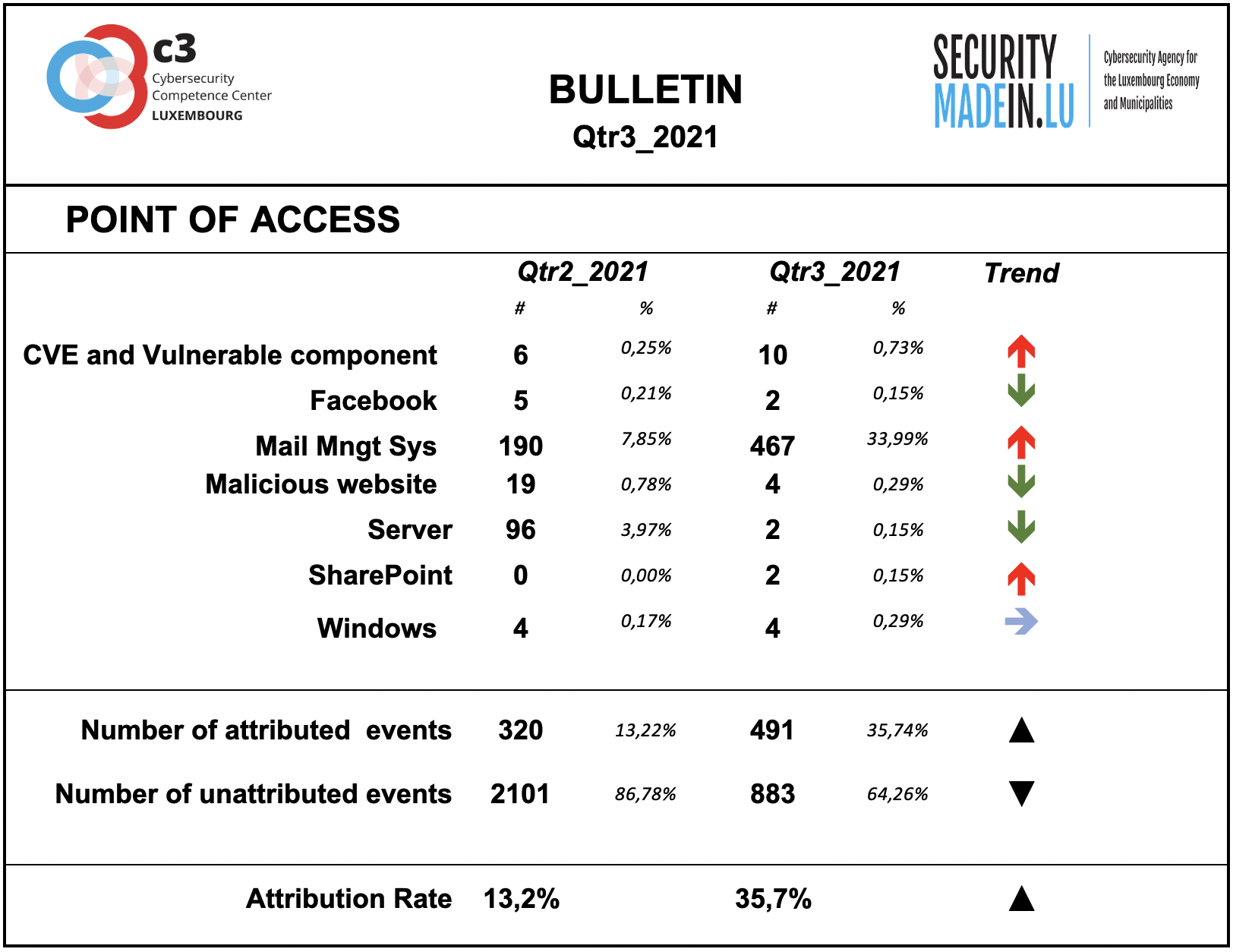
Points of access
The most common access point reported by MISPPRIV users is e-mail, which isn’t too surprising as it’s an effective ingress vector for several types of attacks. It’s often exploiting users’ weaknesses, be they voluntary (negligence) or involuntary (lack of knowledge about a specific threat).
There were also a number of events that took advantage of Facebook and Sharepoint, i.e., a web-based collaborative platform that integrates with Microsoft Office.
There has also been a marked decrease in server utilisation and malicious websites.
However, it’s important to keep in mind that the attribution rate is rather low. Most of the attacks’ point of access is not known.
With regard to component and system vulnerabilities, the monitoring system identified the following:
SolarWinds allows a remote code execution;
Buffalo WSR-2533DHPL2 firmware - authentication vulnerability;
Several vulnerabilities of Microsoft Exchange Server;
ForgeRock AM server - deserialisation vulnerability;
Kaseya VSA allows credential disclosure;
vSphere Client (HTML5) contains several remote code execution vulnerabilities;
Realtek SDK: there are several remotely exploitable vulnerabilities; a Realtek SDK is used in IoT devices sold by a long list of manufacturers that can enable an attacker to gain complete control over an affected device. The flaws affect many popular devices such as IP cameras, routers, WiFi repeaters, and others from manufacturers including Buffalo, ASUS, Belkin, D-Link, LG, Logitec, and Realtek itself;
Several vulnerabilities in Acrobat Reader, iOS, Google Chrome, Windows, Google Chrome, Microsoft Exchange;
Trend Micro Apex One has an improper input validation vulnerability;
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Fabric Switches in Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) Mode could allow the generation of DoS type of attack.
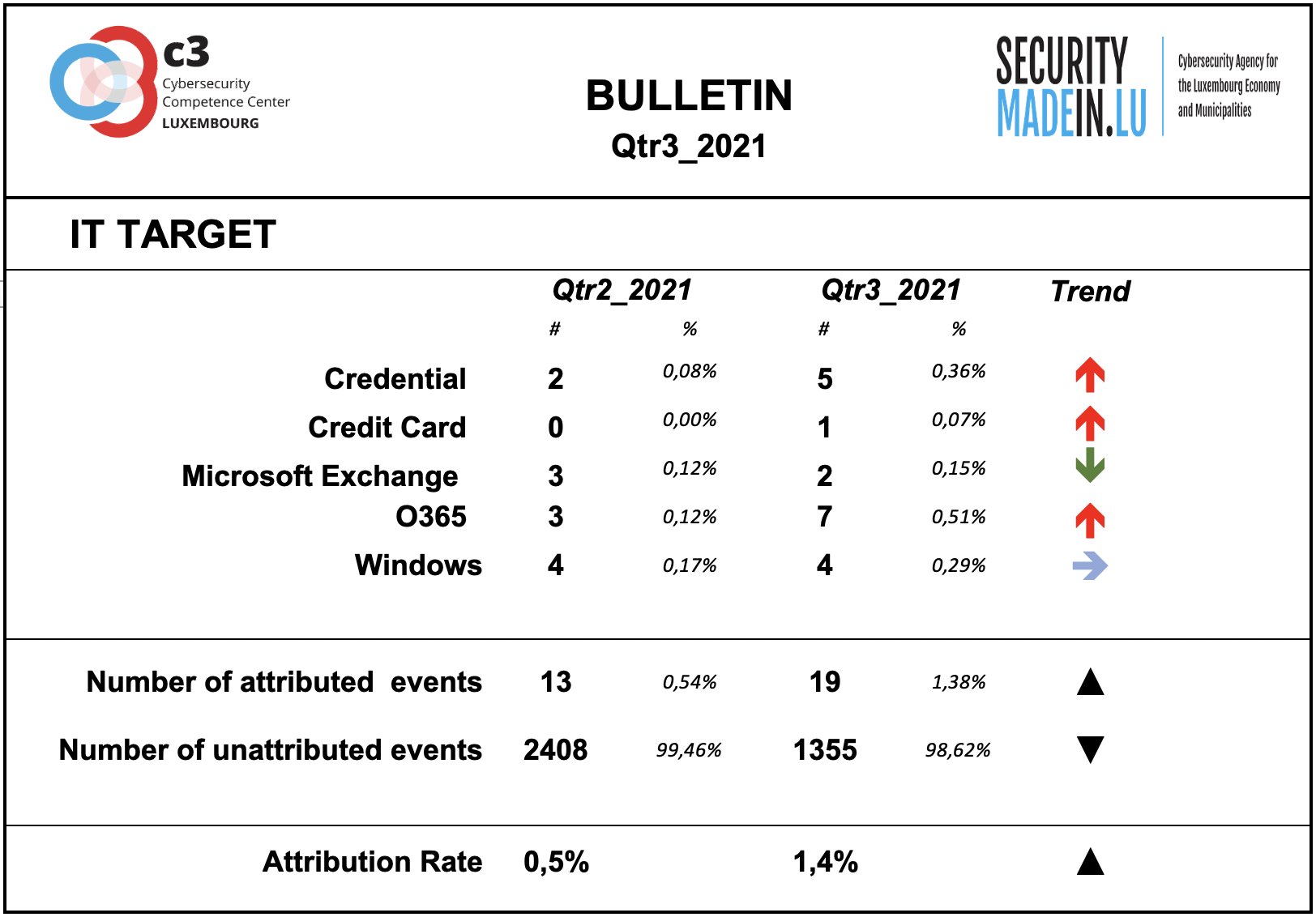
IT Target
Information on the attacked IT target is not sufficiently described by the analysed events.
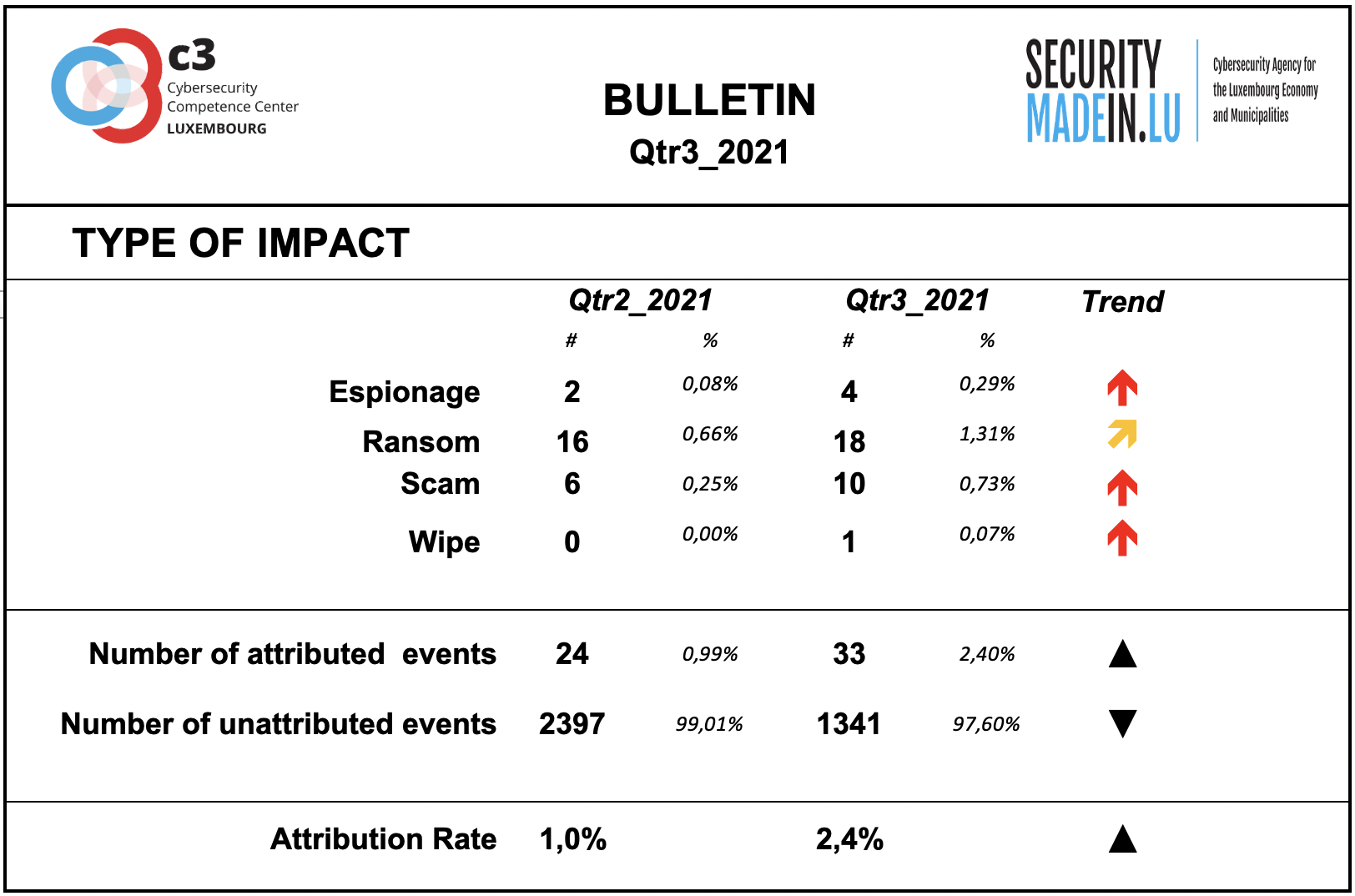
Type of Impact
Information on the type of consequences for the victim is mainly related to ransom demands.
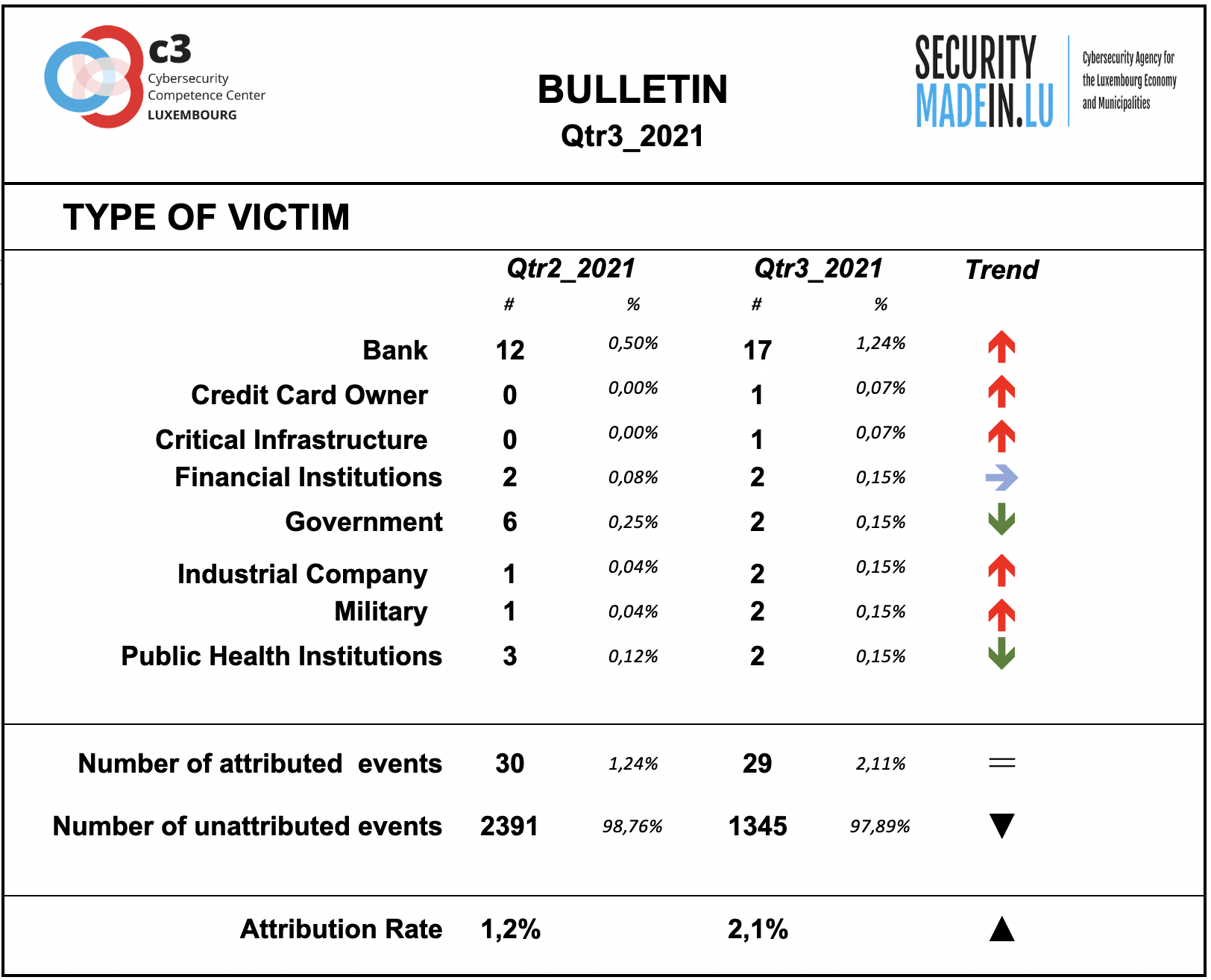
Type of Victim
There has been a continuation of attacks on banks and other institutions.