2021 - IV Quarterly Bulletin
NC3 TOP – Threat Observatory Platform
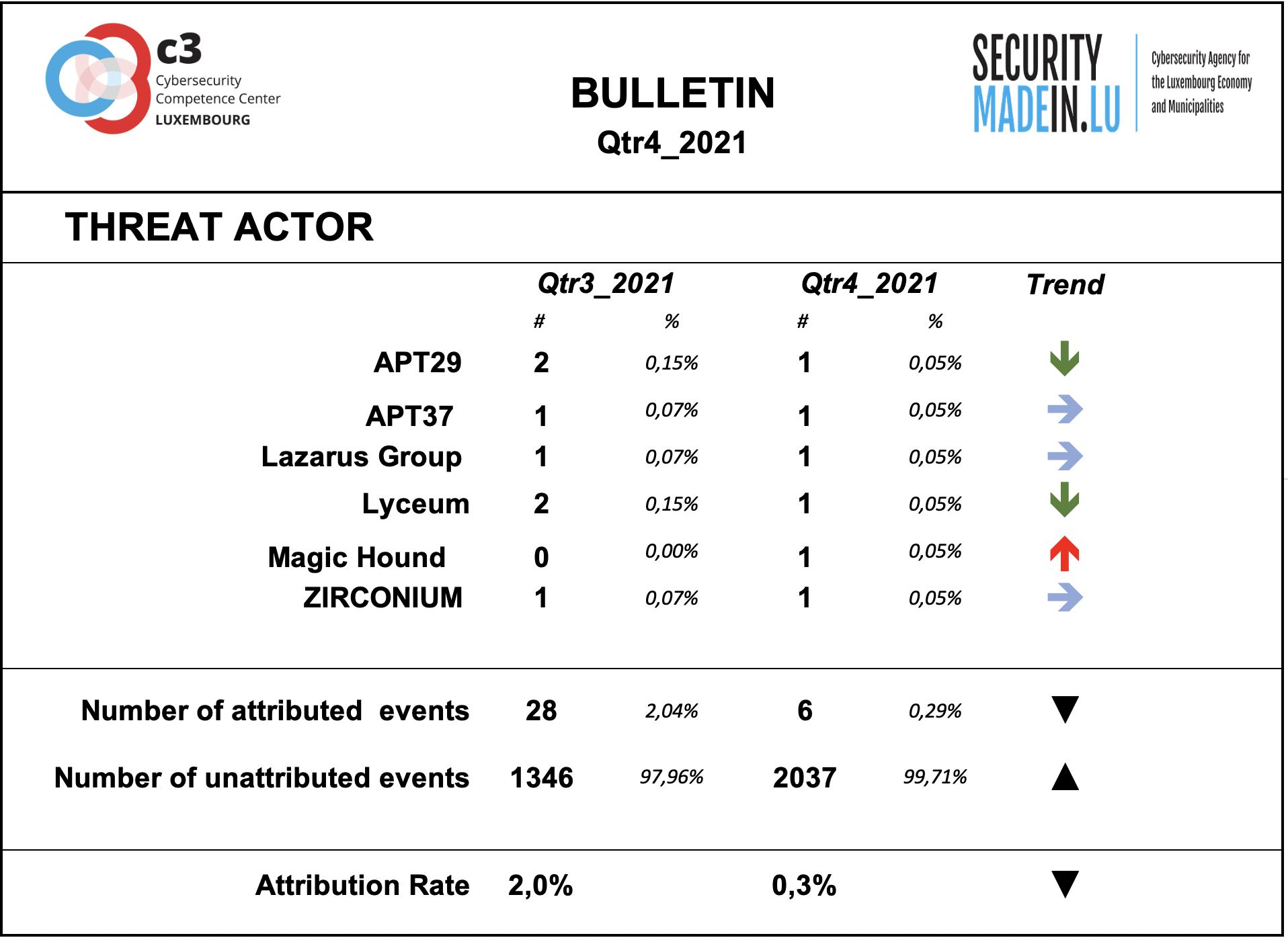
Threat Agent activities
Behind every cyber-attack there is an actor with a specific intent. However, for many events, the identity and general motivation are unknown. On the other hand, some groups have been well known for years and their criminal activities and techniques are documented and monitored. Typically, they conduct targeted attacks against specific organisations, using relatively sophisticated tools and attack procedures.
Some of them are considered as State-sponsored, but the actual link with various countries stays often subject of controversies and should be considered with prudence.
During the fourth quarter of 2021 the monitoring system recorded a decrease of identifiable threat groups’ activity.
As during previous quarters, the attribution rate of events is very low. This means that most of the ongoing attacks are not attributable.
According to the attribution found in the MISP records, the following groups were particularly active during this quarter:
APT29 is a Russian hacker group believed to be associated with one or more intelligence agencies of Russia; it primarily targets Western governments and related organizations, such as government ministries and agencies, political think tanks, and governmental subcontractors;
APT37 is a North Korean state-sponsored cyber espionage group that has been active since at least 2012. The group has targeted victims primarily in South Korea, but also in Japan, Vietnam, Russia, Nepal, China, India, Romania, Kuwait, and other parts of the Middle East;
Lazarus group is a North Korean state-sponsored cyber threat group; it uses a wide range of methods depending on the characteristics of the campaigns carried out and the objectives pursued. It mainly aimed at manipulating employees of strategically important companies such as those involved in the military or aerospace industry;
Lyceum is an emerging threat to energy organizations in the Middle East, but it should not assume that future targeting will be limited to this sector. Lyceum 's targeting of telecommunications has been speculated to be part of an effort to establish man-in-the-middle capabilities throughout the Middle East region;
Magic Hound is an Iranian-sponsored threat group that conducts long term, resource-intensive cyber espionage operations, likely on behalf of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps. They have targeted U.S. and Middle Eastern government and military personnel, academics, journalists, and organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO), via complex social engineering campaigns since at least 2014;
ZIRCONIUM is a threat group operating out of China, active since at least 2017, that has targeted individuals associated with the 2020 US presidential election and prominent leaders in the international affairs community.
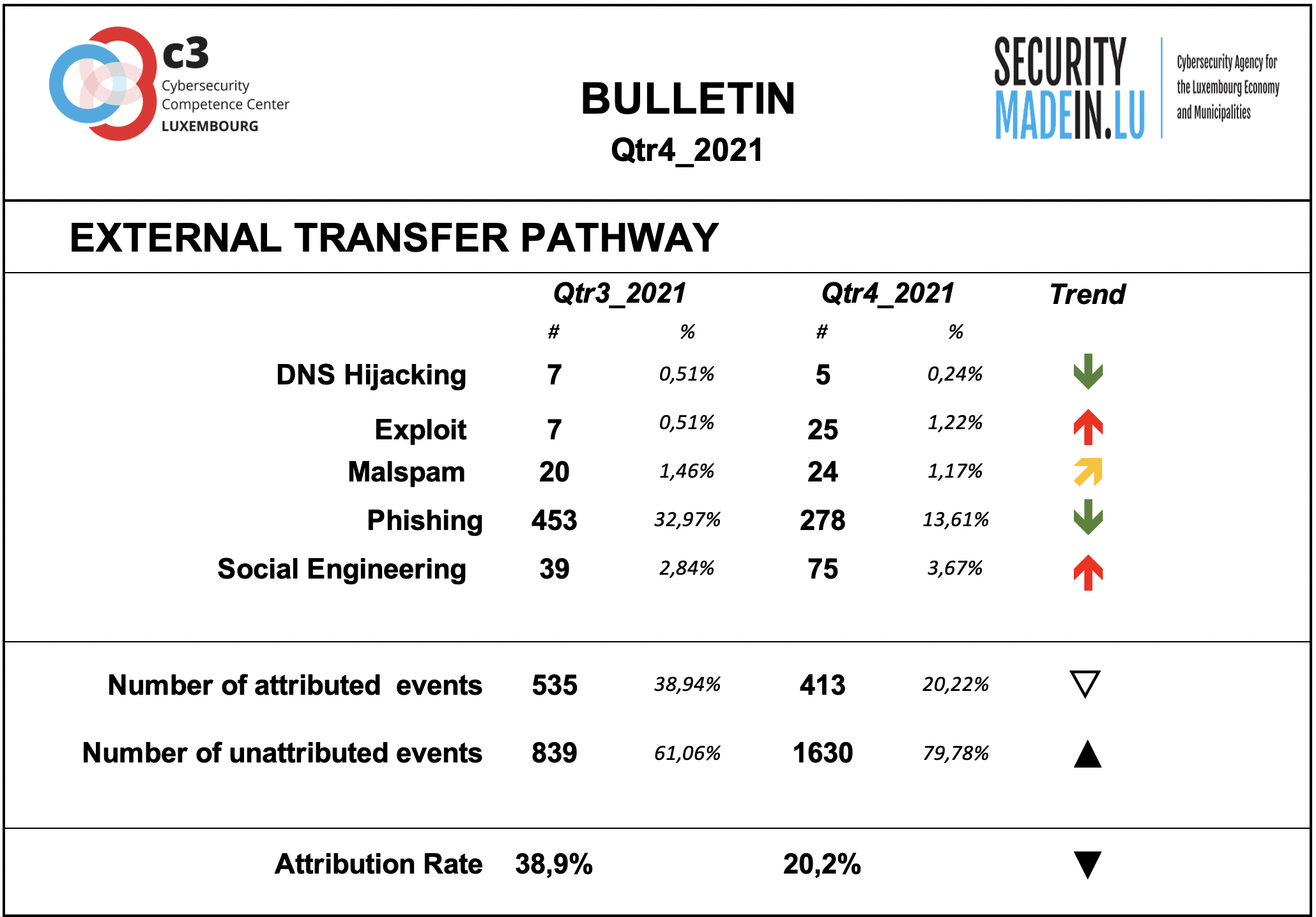
External transfer pathway and infrastructures
The transfer of the malicious artefacts or payloads is done through a number of different types of technical procedures and infrastructures.
Also, during the fourth quarter of 2021, the monitoring system revealed and confirmed confirmed that the most frequently used strategy is associated with scams that use email or similar approaches to reach potential victims.
Phishing is the most common strategy, but there has also been an increase in exploit, i.e., activities that allows to leverage a vulnerability.
The high number of exploits are mainly associated with the exploitation of the Apache Log4j, a Java-based logging utility.
The attribution rates are significantly better than for threat actors, even if still fairly low. Attribution means that it was possible to identify the external transfer pathway for a given event.
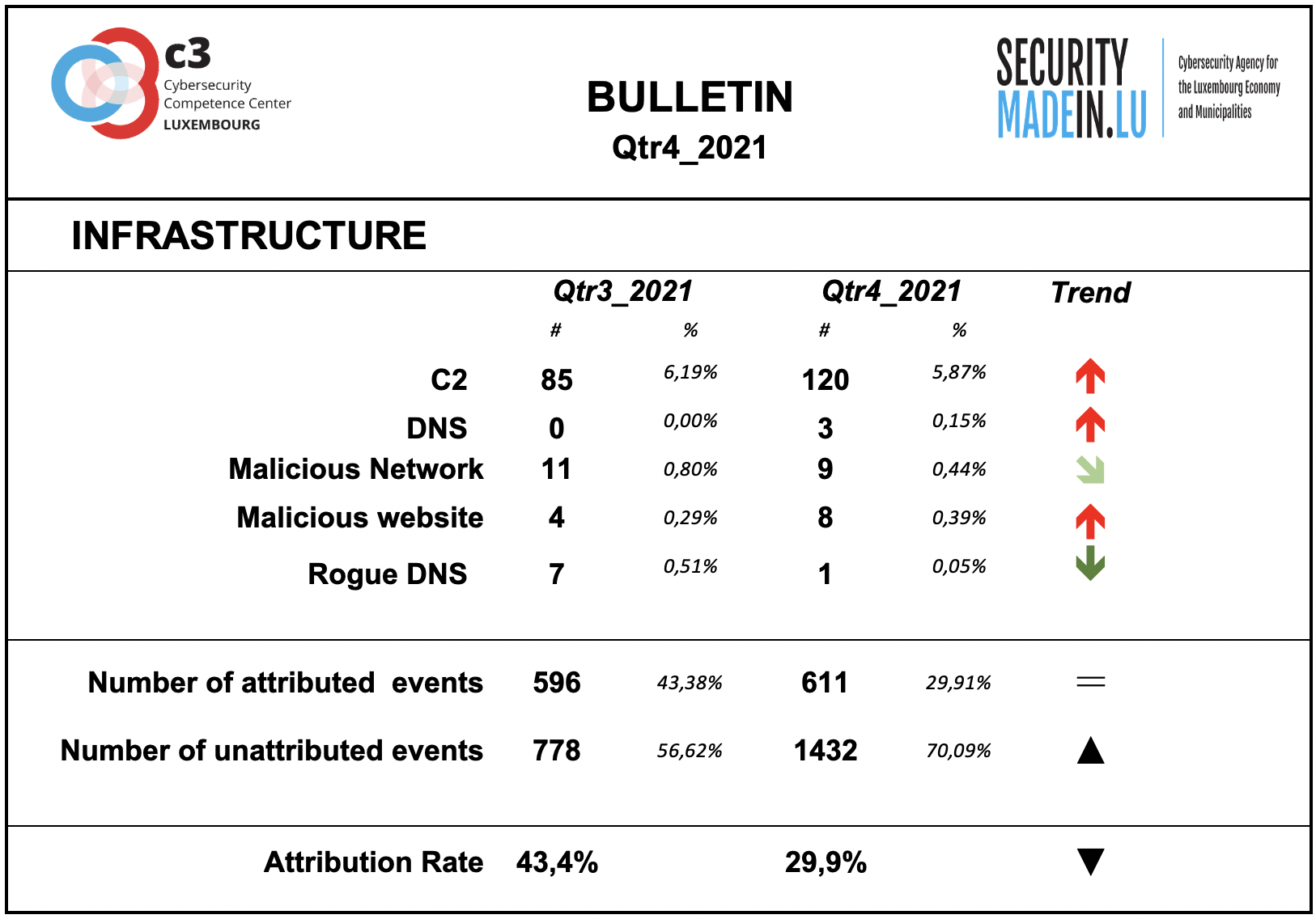
Infrastructures represent the type of systems being used for supporting attacks. Some are meant to compromise or help compromise, the targeted system, others are more focused on helping to maintain the foothold in it. Indeed, once access to a system device has been gained, a communication channel is maintained through the use of command and control (C2) infrastructures. The specific mechanisms vary greatly between attacks, but C2 generally consists of one or more covert communication channels between devices in a victim organization and a platform that the attacker controls. These communication channels are supporting the malicious activities. They are used to issue instructions to the compromised devices, download additional malicious payloads, and pipe stolen data back to the cyber-actor.
During this period, there was an increase in the use of C2 infrastructures and in the use of malicious websites.
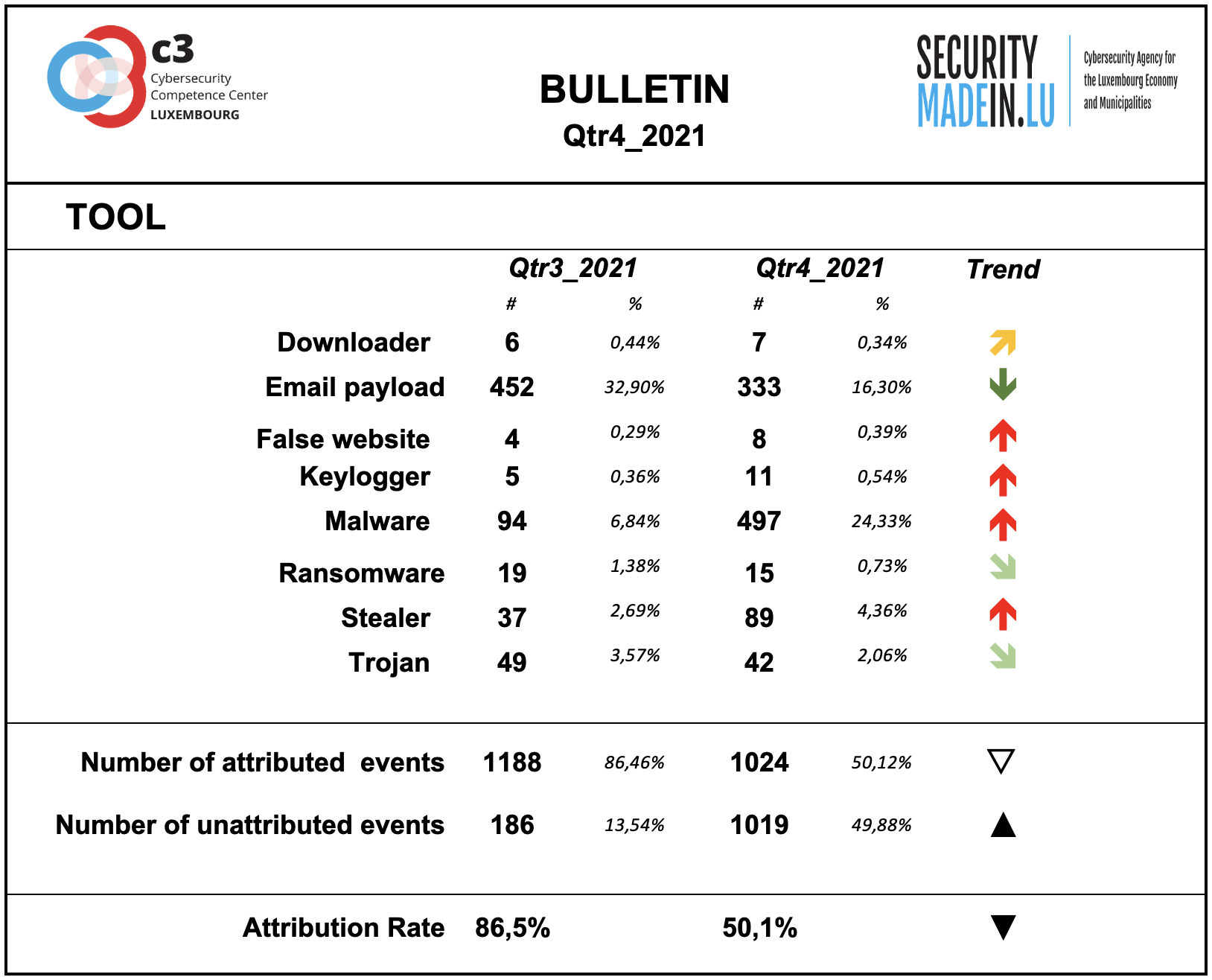
Tool
The monitoring system showed a substantial prevalence of the use of Malware especially associated with IoT systems.
During this quarter, there was a slight decrease in the number of ransomware attacks and a significant increase in malware.
Compared to the other dimensions of the interpretation model, this dimension confirms itself as the one with the highest rate of attribution, even if this quarter shows a significant decrease compared to the previous one.
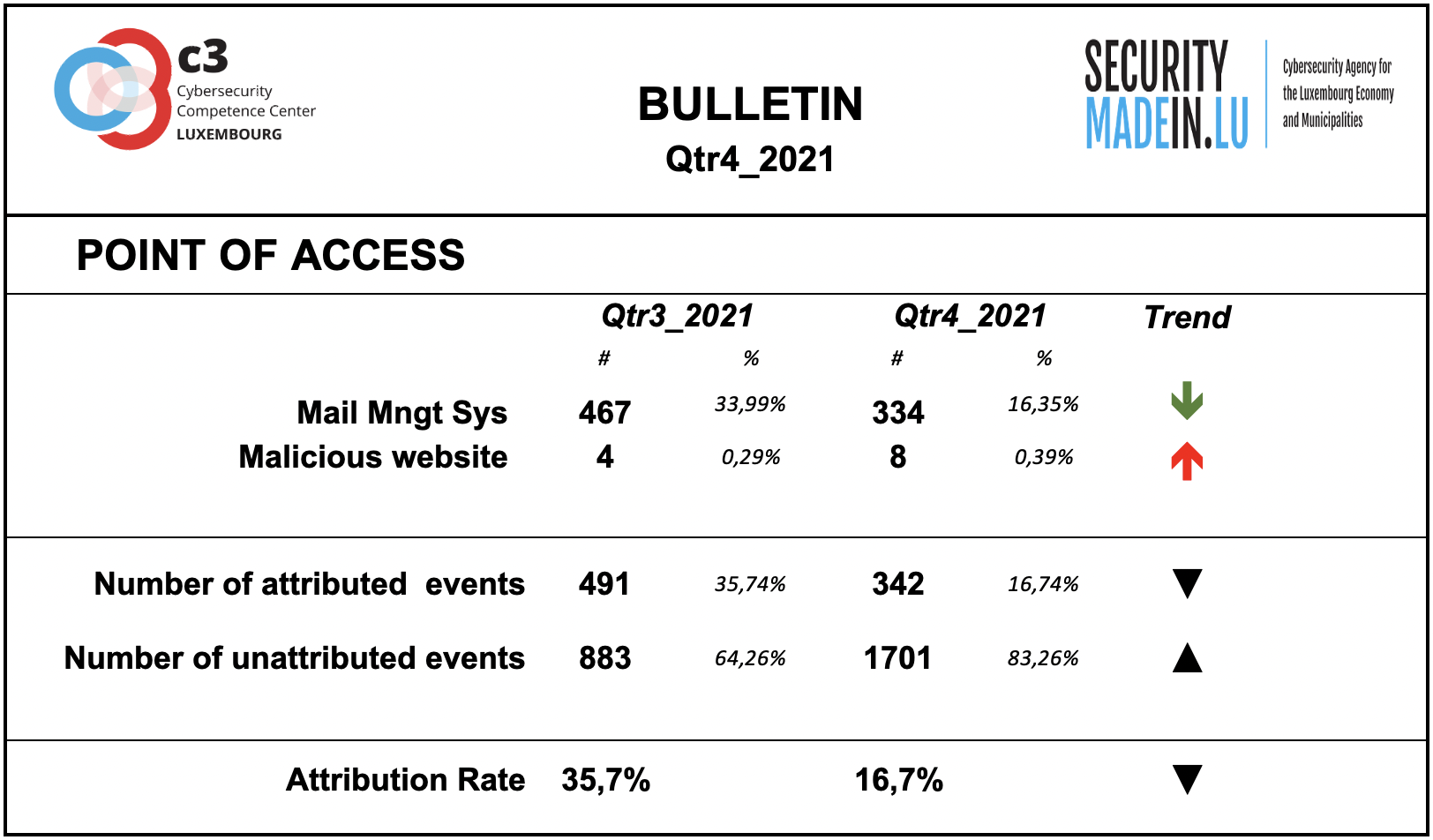
Points of access
The most common access point reported by MISPPRIV users is e-mail, which isn’t too surprising as it’s an effective ingress vector for several types of attacks. It’s often exploiting users’ weaknesses, be they voluntary (negligence) or involuntary (lack of knowledge about a specific threat).
However, it’s important to keep in mind that the attribution rate is rather low. Most of the attacks’ point of access is not known.
With regard to component and system vulnerabilities, the monitoring system identified the following:
- Zoho Manage Engine is vulnerable to REST API authentication bypass;
GitLab has vulnerabilities that allow remote command execution;
BQE BillQuick Web Suite has vulnerabilities that allow SQL injection remote command execution;
Yealink Device Management has vulnerabilities that allow command injection;
- Vulnerability of the Apache HTTP Server;
- Several vulnerabilities of Google Chrome.
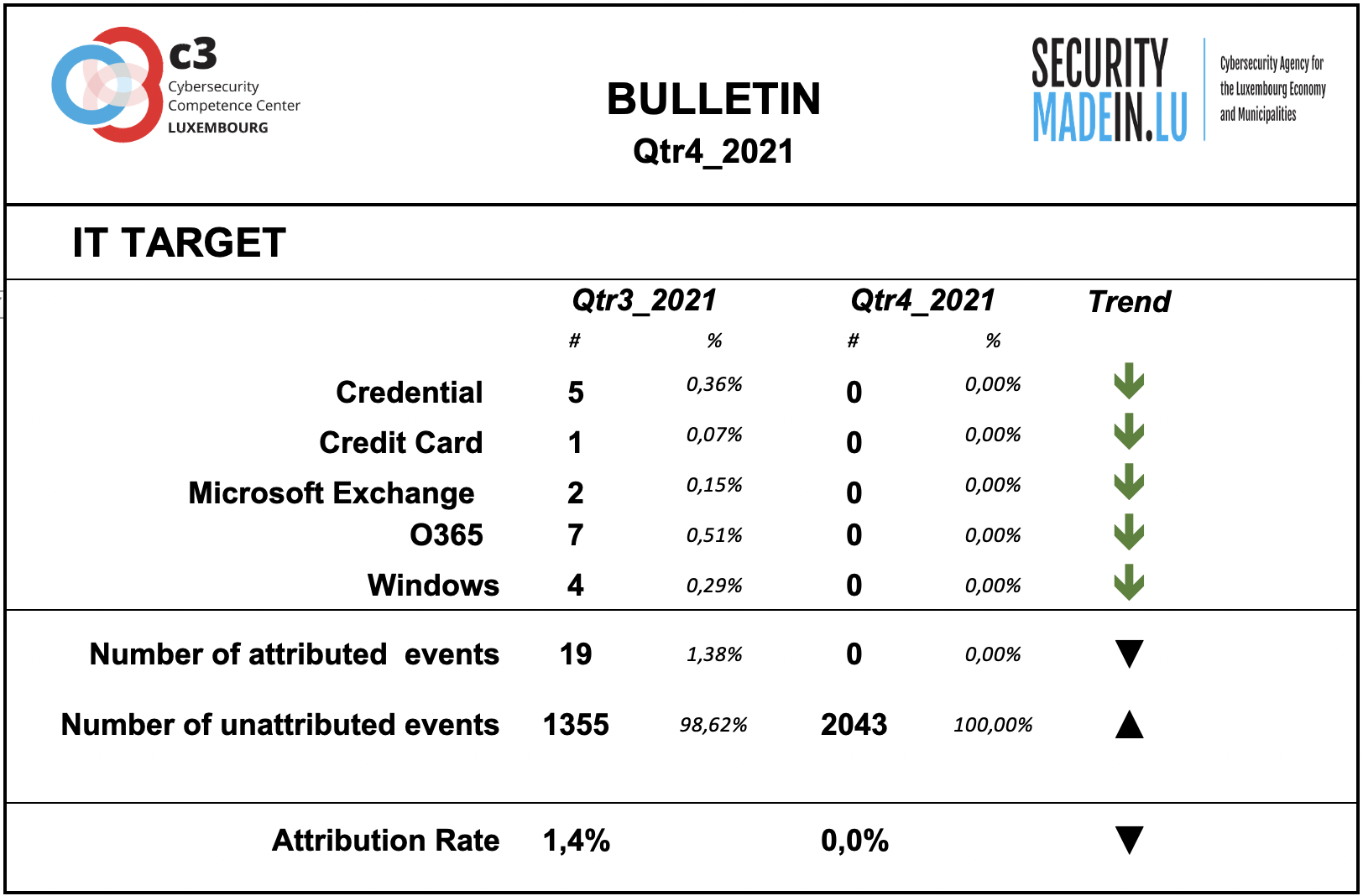
IT Target
Information on the attacked IT target is not sufficiently described by the analysed events.
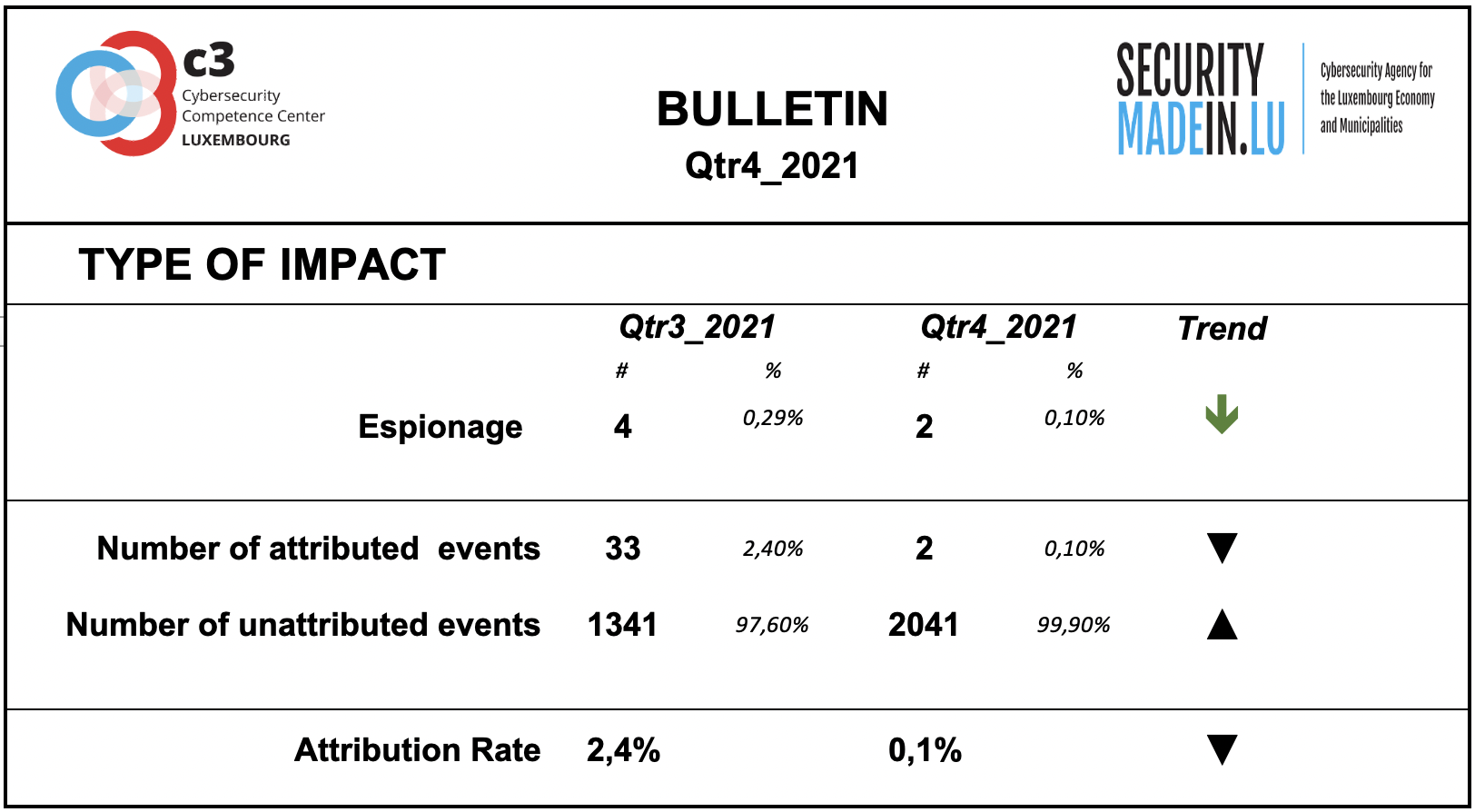
Type of Impact
Information on the type of consequences for the victim is mainly related to ransom demands, although fewer events were recorded than in the previous quarter.
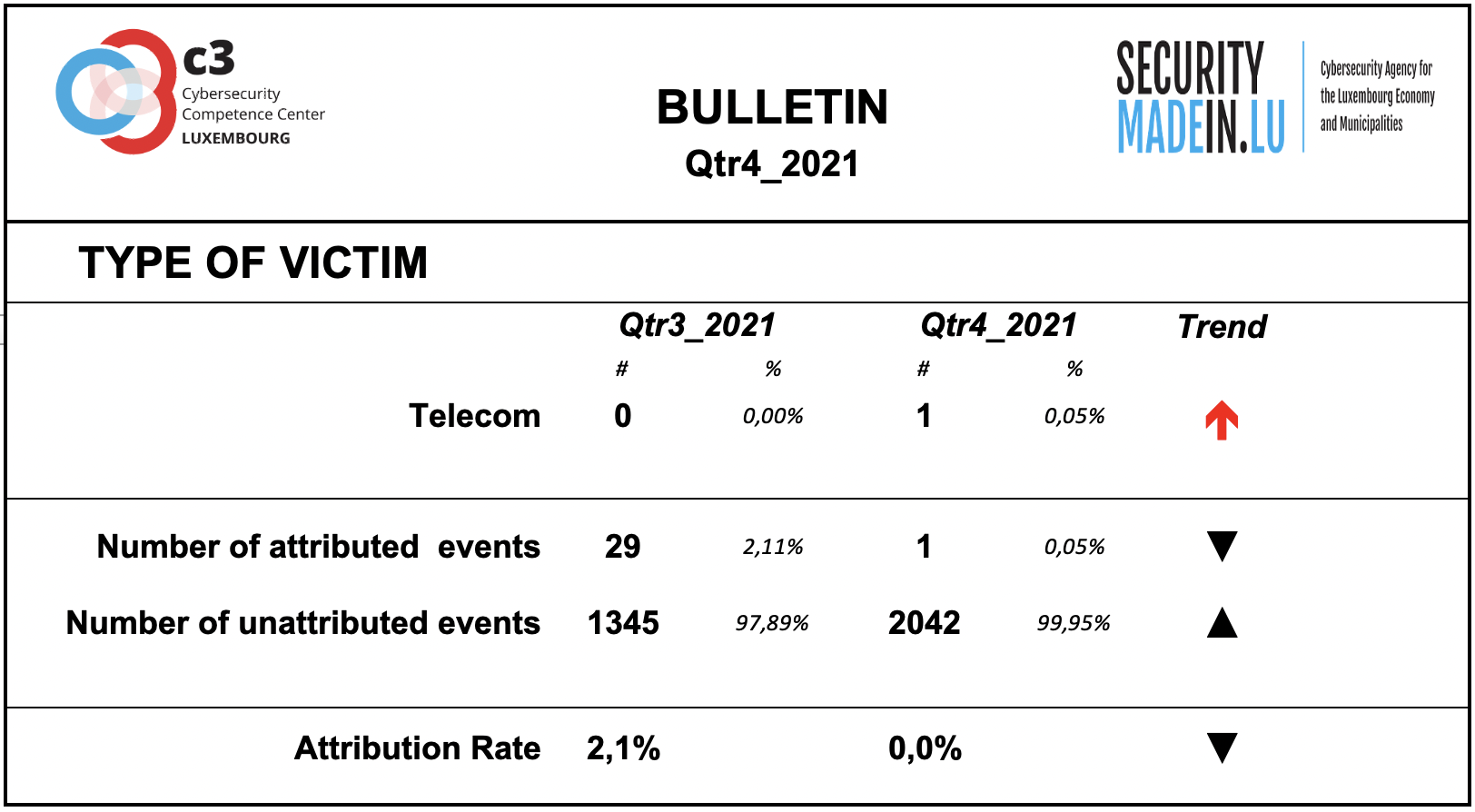
Type of Victim
There was a continuation of attacks on airlines, although compared to previous quarters, the monitoring system showed a decrease.
Attacks on banks and critical infrastructure systems are still in evidence.