2022 - I Quarterly Bulletin
NC3 TOP – Threat Observatory Platform
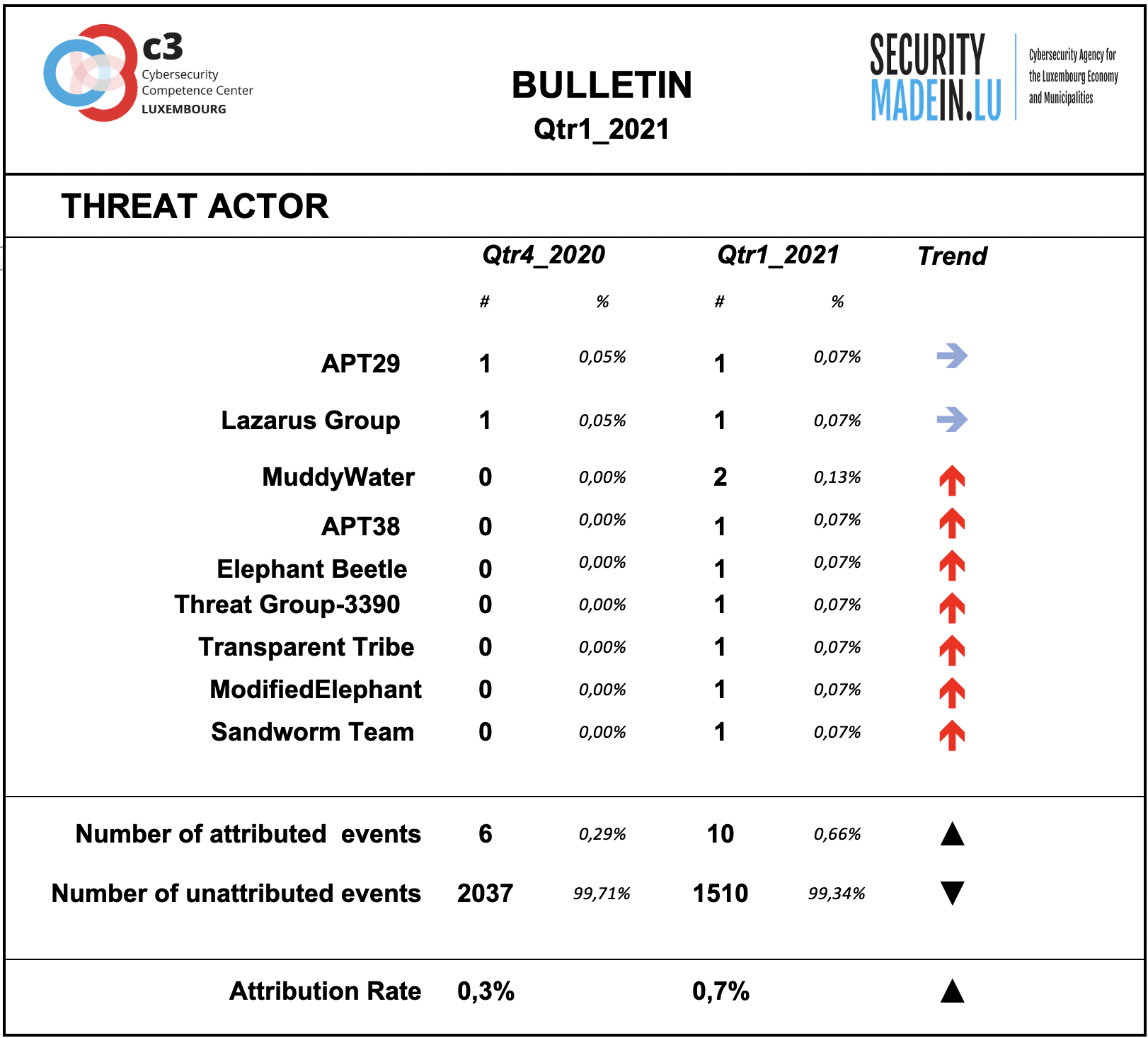
Threat Agent activities
Behind every cyber-attack there is an actor with a specific intent. However, for many events, the identity and general motivation are unknown. On the other hand, some groups have been well known for years and their criminal activities and techniques are documented and monitored. Typically, they conduct targeted attacks against specific organisations, using relatively sophisticated tools and attack procedures.
Some of them are considered as State-sponsored, but the actual link with various countries stays often subject of controversies and should be considered with prudence.
As during previous quarters, the attribution rate of events is very low. This means that most of the ongoing attacks are not attributable.
According to the attribution found in the MISP records, the following groups were particularly active during this quarter:
APT29: is a Russian hacker group believed to be associated with one or more intelligence agencies of Russia; it primarily targets Western governments and related organizations, such as government ministries and agencies, political think tanks, and governmental subcontractors;
Lazarus group is a North Korean state-sponsored cyber threat group; it uses a wide range of methods depending on the characteristics of the campaigns carried out and the objectives pursued. It mainly aimed at manipulating employees of strategically important companies such as those involved in the military or aerospace industry;
MuddyWater is an Iranian threat group that has primarily targeted Middle Eastern nations, and has also targeted European and North American nations. The group's victims are mainly in the telecommunications, government (IT services), and oil sectors;
APT38 is a North Korean state-sponsored threat group that specializes in financial cyber operations.
Elephant Beetle group is base in Latin America and it blends into an environment before loading up trivial, thickly stacked, fraudulent financial transactions too tiny to be noticed but adding up to millions of dollars.
Threat Group-3390 is a Chinese threat group that has extensively used strategic Web compromises to target victims. A China-based actor that targets foreign embassies to collect data on government, defence, and technology sectors.
Transparent Tribe is a suspected Pakistan-based threat group that has been active since at least 2013, primarily targeting diplomatic, defence, and research organizations in India and Afghanistan.
ModifiedElephant APT is responsible for targeted attacks on human rights activists, human rights defenders, academics, and lawyers across India with the objective of planting incriminating digital evidence. ModifiedElephant has been operating since at least 2012, and has repeatedly targeted specific individuals.
Sandworm Team is a destructive threat group that has been attributed to Russia's General Staff Main Intelligence Directorate (GRU) Main Center for Special Technologies (GTsST) military unit 74455. This group has been active since at least 2009. In October 2020, the US indicted six GRU Unit 74455 officers associated with Sandworm Team for the following cyber operations: the 2015 and 2016 attacks against Ukrainian electrical companies and government organizations, the 2017 worldwide NotPetya attack, targeting of the 2017 French presidential campaign, the 2018 Olympic Destroyer attack against the Winter Olympic Games, the 2018 operation against the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons, and attacks against the country of Georgia in 2018 and 2019. Some of these were conducted with the assistance of GRU Unit 26165, which is also referred to as APT28. Espionage.
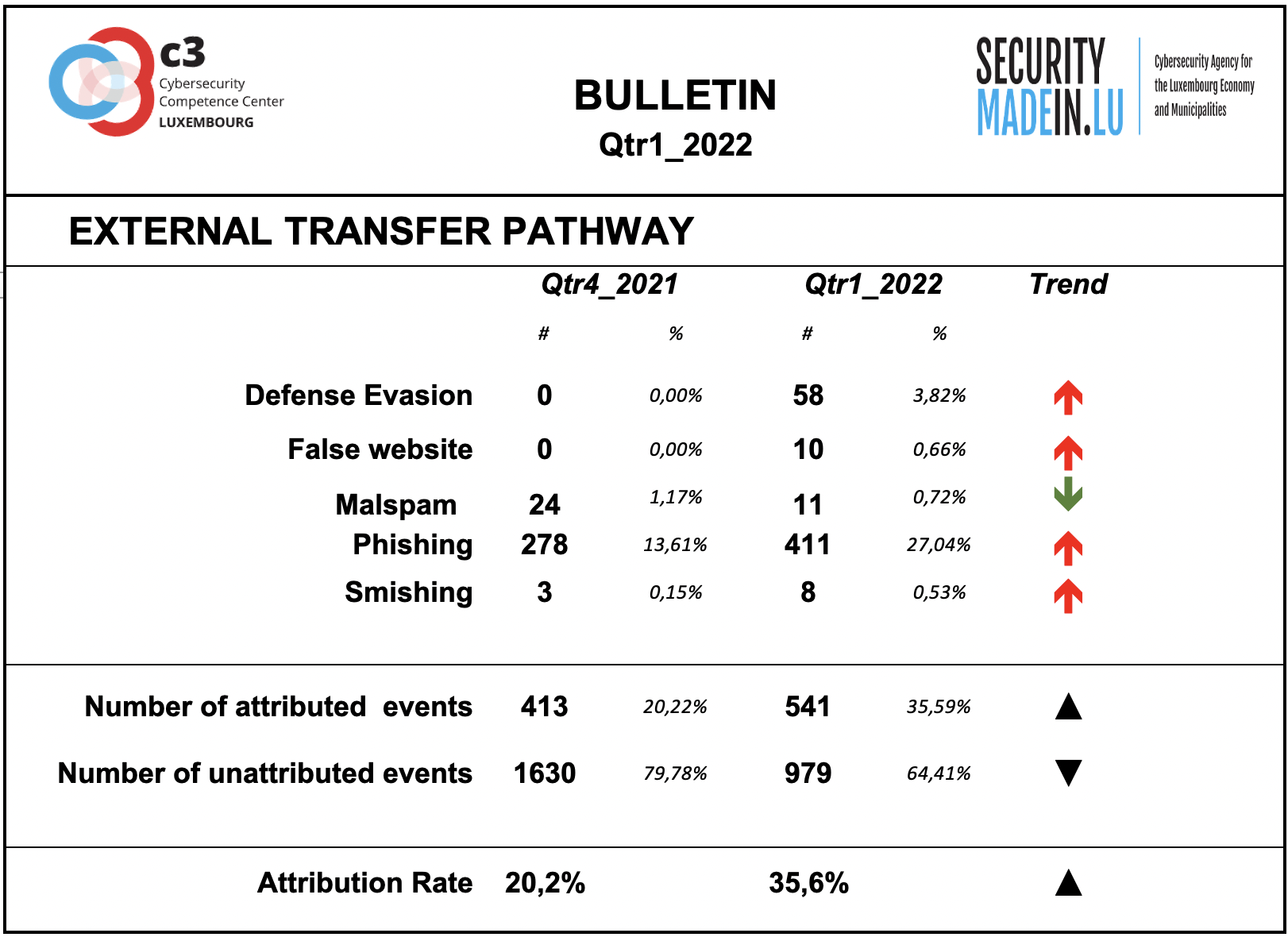
External transfer pathway and infrastructures
The transfer of the malicious artefacts or payloads is done through a number of different types of technical procedures and infrastructures.
Also, during the first quarter of 2022, it is confirmed that the most frequently used strategy is associated with scams that use email or similar approaches to reach potential victims.
Phishing is the most common strategy and during this quarter a significant increase has been recorded. In most of these cases, the pathway is a human to human or machine to human infrastructure.
There is also a significant increase in the number of events implementing defence evasion strategies, i.e. techniques to avoid, disable or subvert trusted security software or processes in order to hide or to mask their malware.
The attribution rates are significantly better than for threat actors, even if still fairly low. Attribution means that it was possible to identify the external transfer pathway for a given event.
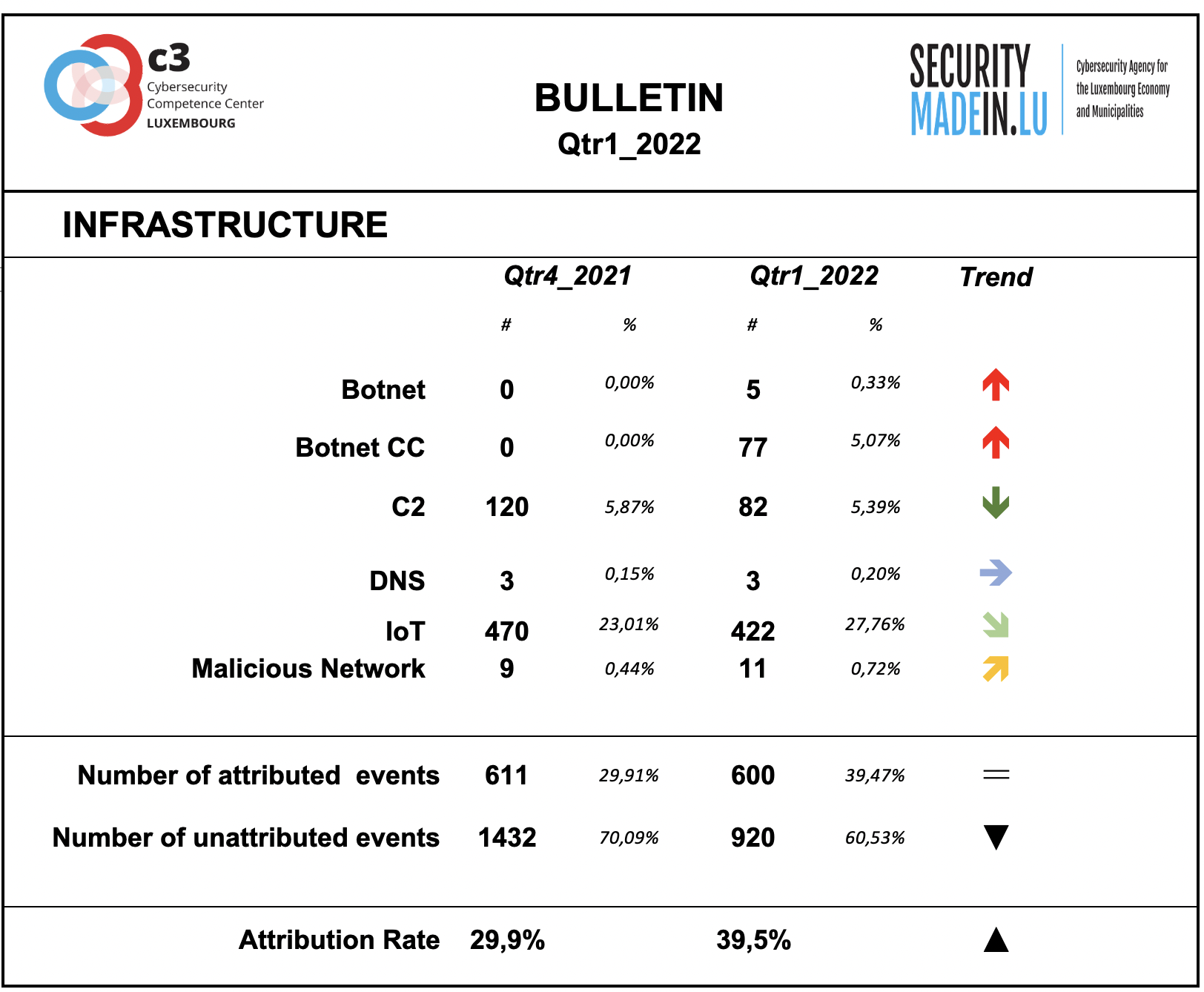
Infrastructures represent the type of systems being used for supporting attacks. Some are meant to compromise or help compromise, the targeted system, others are more focused on helping to maintain the foothold in it. Indeed, once access to a system device has been gained, a communication channel is maintained through the use of command and control (C2) infrastructures. The specific mechanisms vary greatly between attacks, but C2 generally consists of one or more covert communication channels between devices in a victim organization and a platform that the attacker controls. These communication channels are supporting the malicious activities. They are used to issue instructions to the compromised devices, download additional malicious payloads, and pipe stolen data back to the cyber-actor.
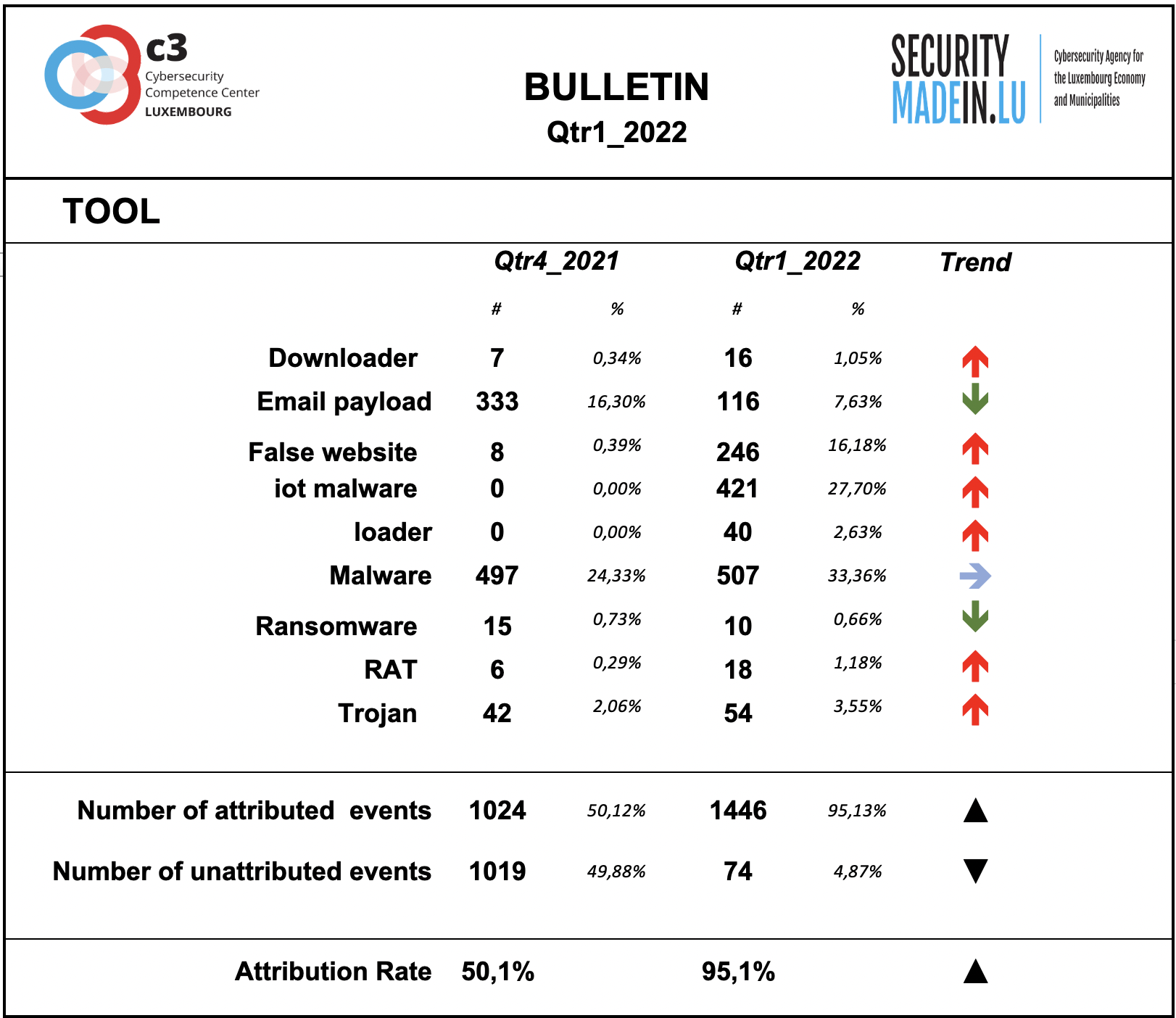
Tool
The monitoring system showed a substantial prevalence of the use of Malware especially associated with IoT systems.
During this quarter, there was an increase of event that used downloader and loader tools. Instead, the number of ransomware attacks decreased.
Compared to the other dimensions of the interpretation model, this dimension is confirmed as having the highest attribution rate.
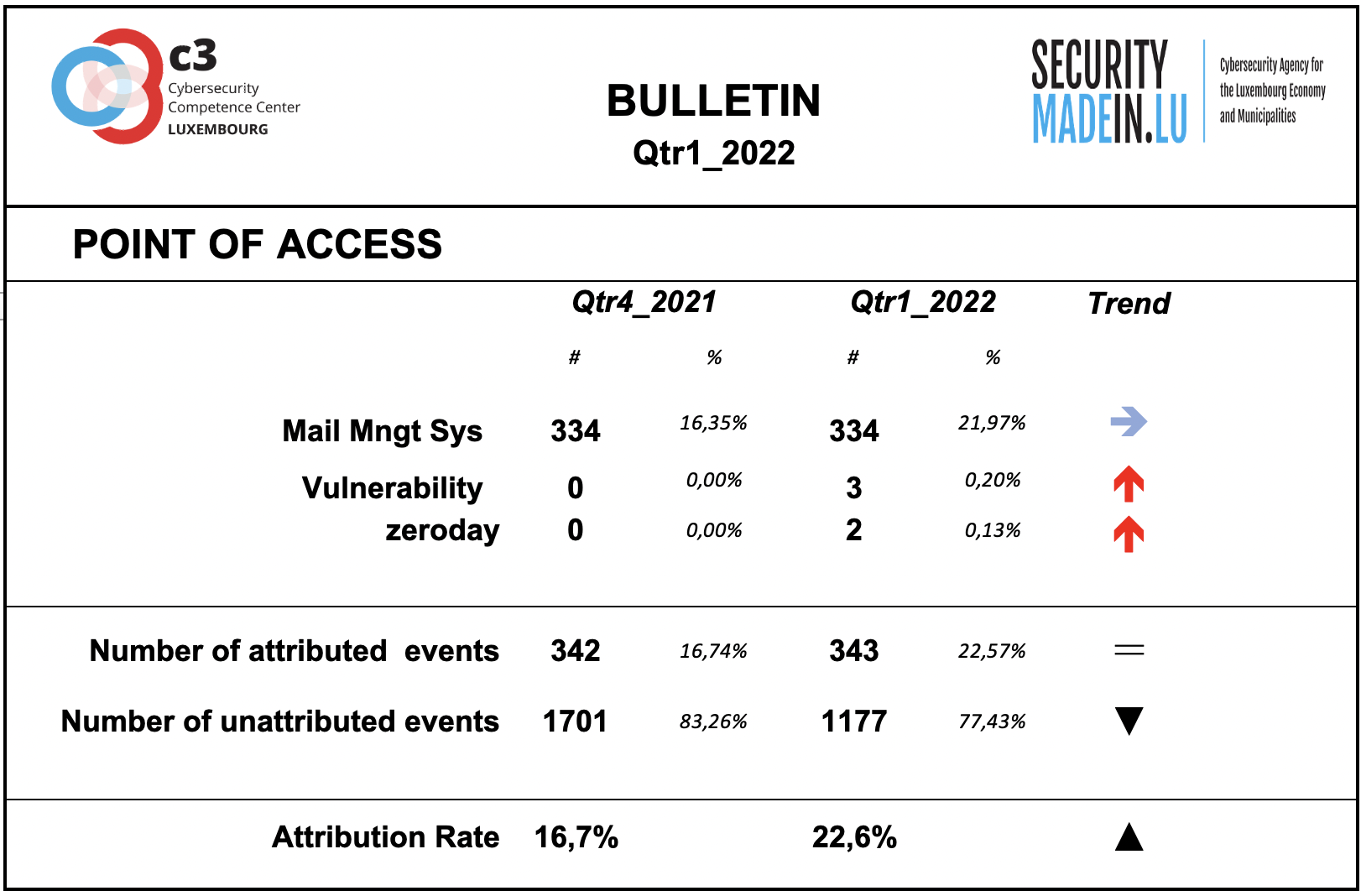
Points of access
The most common access point reported by MISPPRIV users is e-mail, which isn’t too surprising as it’s an effective ingress vector for several types of attacks. It’s often exploiting users’ weaknesses, be they voluntary (negligence) or involuntary (lack of knowledge about a specific threat.
It should be noted the many attack strategies using scam websites will typically relay on phishing technique to drive victims towards false website. False website may be used then to still private information or to infect user's devices with malicious software for various purposes. Very often the first approach to redirect victims to fake websites is through phishing e-mail.
However, it’s important to note that the attribution rate of this dimension is rather low, i.e. most of the attacks’ point of access is not known.
With regard to component and system vulnerabilities, the monitoring system identified the following:
Multiple vulnerabilities in VMware Carbon Black App Control were reported. Improper input validation process may lead to remote code execution. Patches are available.
Unpatched FortiGate SSL-VPN devices (CVE-2018-13379) allowed malicious actors to obtain credentials; Credentials can also be obtained from patched systems that have not changed their passwords after the update.
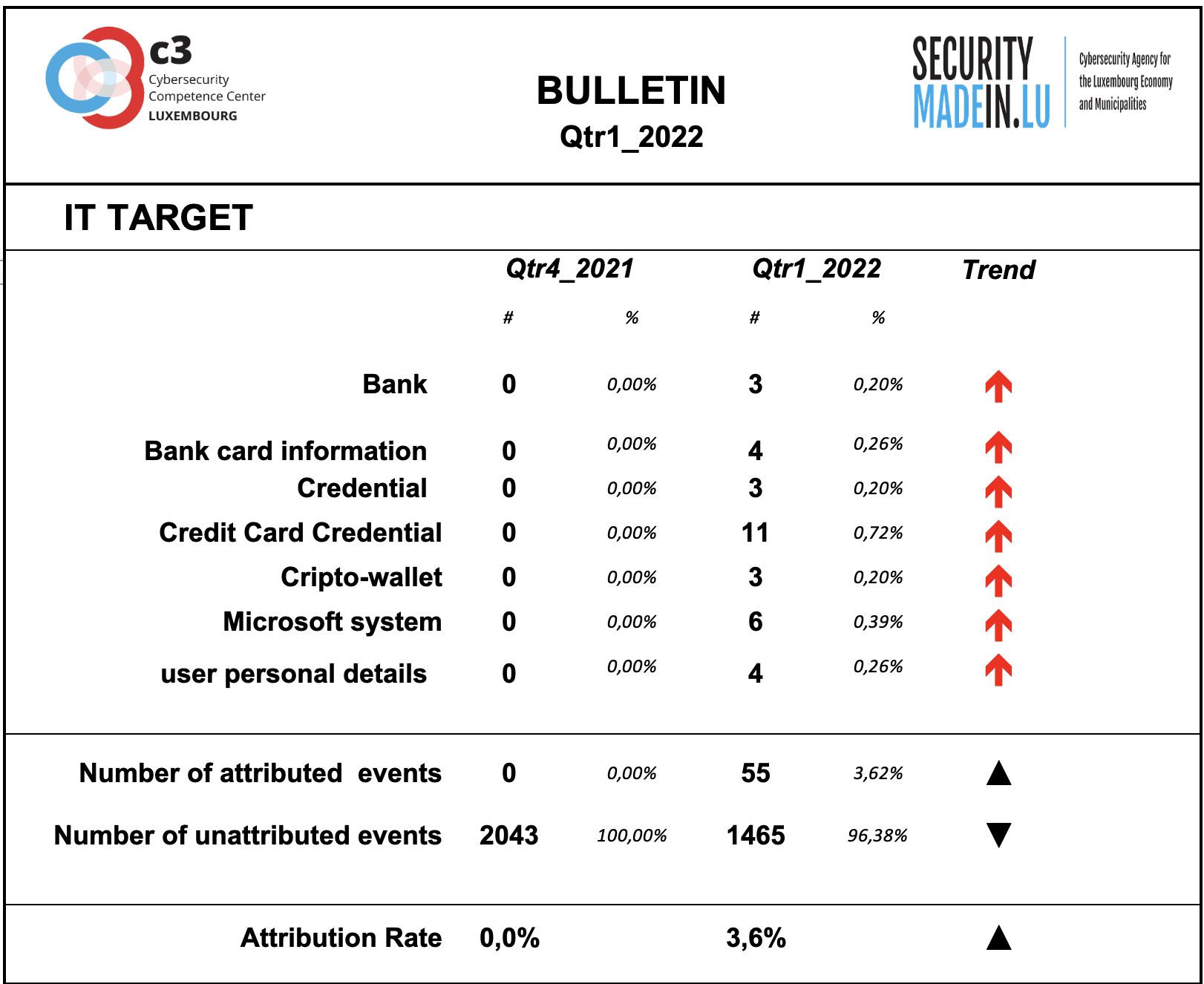
IT Target
Information on the attacked IT target is not sufficiently described by the analysed events.
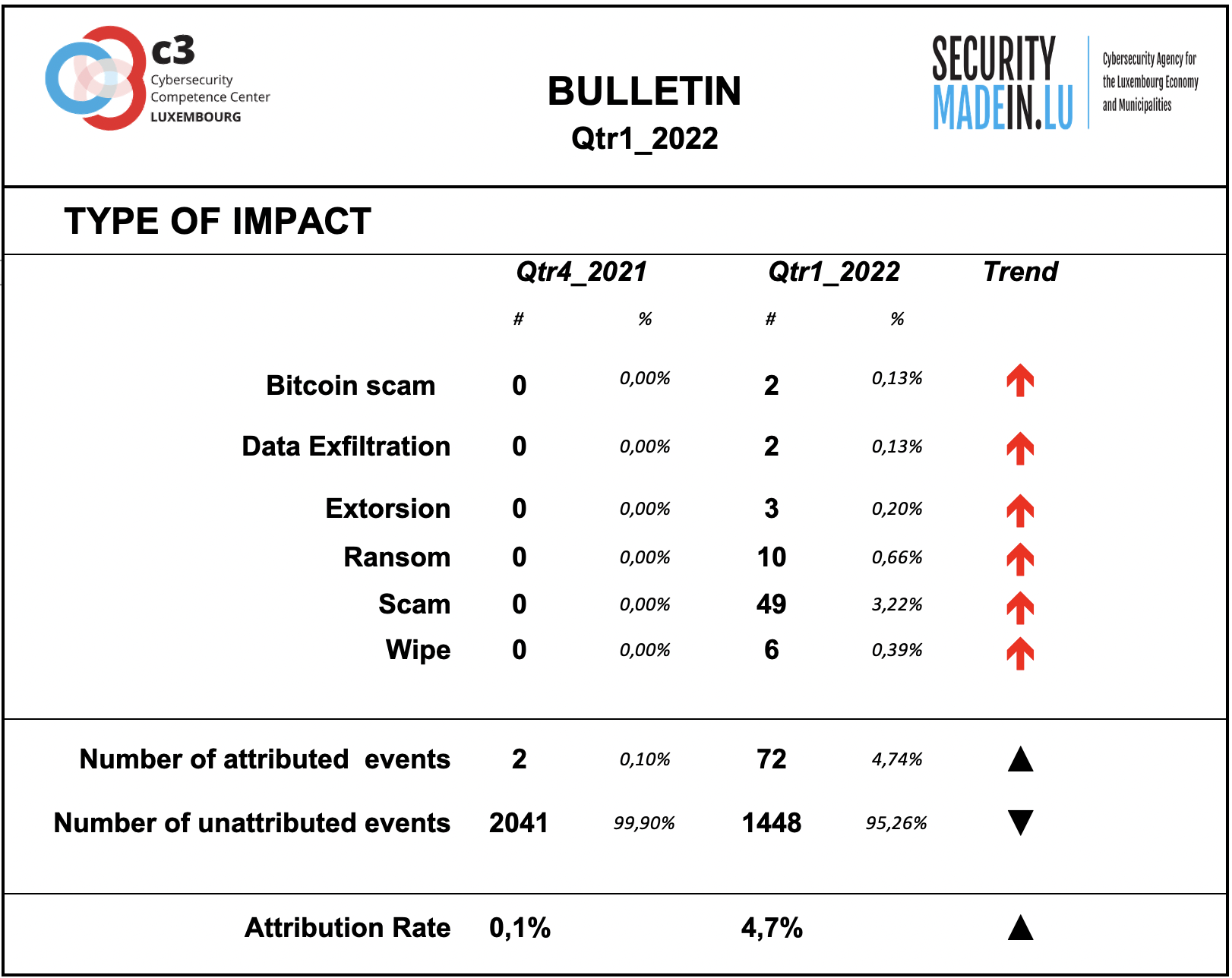
Type of Impact
Information on the type of consequences for the victim is mainly related to ransom demands, although fewer events were recorded than in the previous quarter.
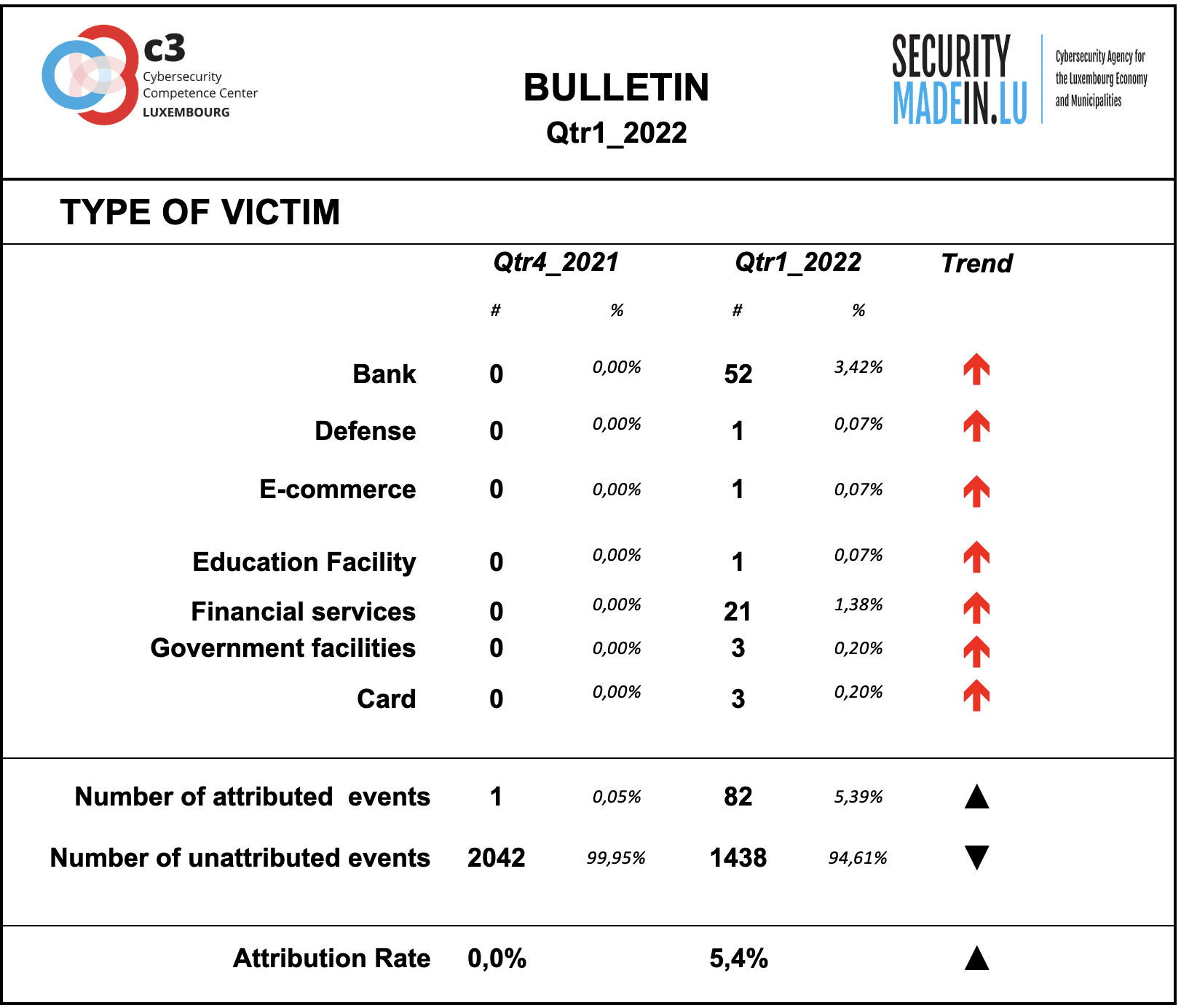
Type of Victim
During this quarter, attacks on banking and financial institutions are prevalent.