2022 - IV Quarterly Bulletin
NC3 TOP – Threat Observatory Platform
Threat Agent activities
Behind every cyber-attack there is an actor with a specific intent. However, for many events, the identity and general motivation are unknown. On the other hand, some groups have been well known for years and their criminal activities and techniques are documented and monitored. Typically, they conduct targeted attacks against specific organisations, using relatively sophisticated tools and attack procedures.
Some of them are considered as State-sponsored, but the actual link with various countries stays often subject of controversies and should be considered with prudence.
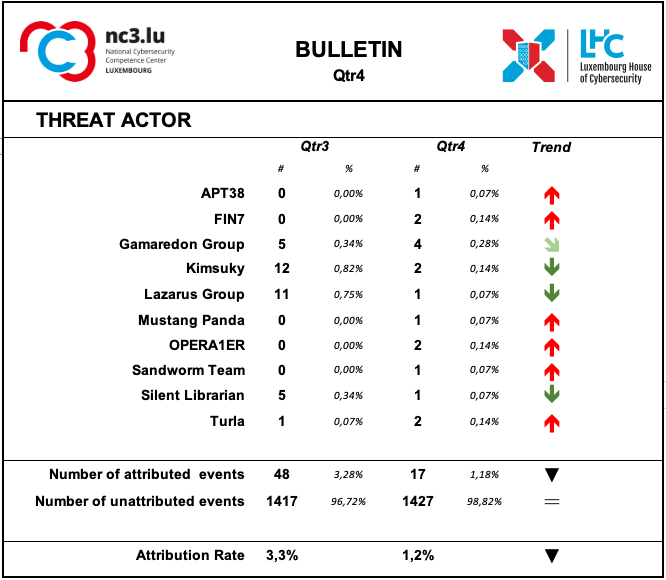
Based on the MISP system's collections, in the fourth quarter of 2022, a substantial decrease in the number of recognised activities of identifiable threat groups was observed.
As during previous quarters, the attribution rate of events is very low. This means that most of the ongoing attacks are not attributable.
According to the attribution found in the MISP records, the following groups were active during this quarter:
APT38 is a North Korean state-sponsored threat group that specializes in financial cyber operations;
FIN7 is a financially-motivated threat group that has been active since 2013 primarily targeting the U.S. retail, restaurant, and hospitality sectors, often using point-of-sale malware;
Gamaredon Group has been active since at least 2013 and has targeted individuals likely involved in the Ukrainian government;
Kimsuky North Korea-based cyber espionage group that has been active since at least 2012. The group initially focused on targeting South Korean government entities, think tanks, and individuals identified as experts in various fields, and expanded its operations to include the United States, Russia, Europe, and the UN. Kimsuky has focused its intelligence collection activities on foreign policy and national security issues related to the Korean peninsula, nuclear policy, and sanctions;
Lazarus group is a North Korean state-sponsored cyber threat group; it uses a wide range of methods depending on the characteristics of the campaigns carried out and the objectives pursued. It mainly aimed at manipulating employees of strategically important companies such as those involved in the military or aerospace industry;
Mustang Panda is a China-based cyber espionage threat actor that was first observed in 2017 but may have been conducting operations since at least 2014. Mustang Panda has targeted government entities, non-profits, religious, and other non-governmental organizations in the U.S., Germany, Mongolia, Myanmar, Pakistan, and Vietnam, among others;
OPERA1ER has repeatedly attacked banks with a basic toolset to execute fraudulent transactions as a part of their phishing campaign. Although African banks were the most frequent victims, highly targeted campaigns have also been observed against many other industries in different geographic regions. Organizations should take steps to mitigate the threat of this highly replicable attack;
Sandworm Team is a destructive threat group that has been attributed to Russia's General Staff Main Intelligence Directorate (GRU) Main Center for Special Technologies (GTsST) military unit 74455. This group has been active since at least 2009;
Silent Librarian is a group that has targeted research and proprietary data at universities, government agencies, and private sector companies worldwide since at least 2013. Members of Silent Librarian are known to have been affiliated with the Iran-based Mabna Institute which has conducted cyber intrusions at the behest of the government of Iran, specifically the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC);
Turla is a Russian-based threat group that has infected victims in over 45 countries, spanning a range of industries including government, embassies, military, education, research and pharmaceutical companies since 2004 is a cyber espionage group operating against targets in East Asia, particularly Taiwan, and occasionally, Japan and Hong Kong. Based on the mutexes and domain names, BlackTech’s campaigns are likely designed to steal their target’s technology.
External transfer pathway and infrastructures
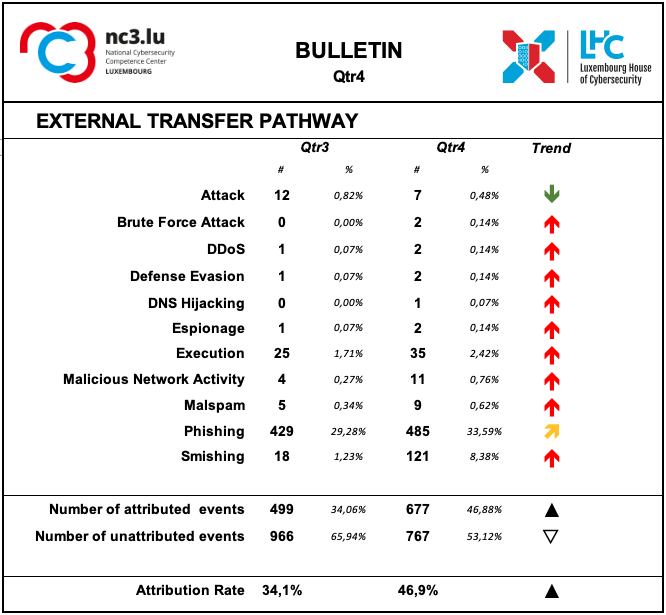
The transfer of the malicious artefacts or payloads is done through a number of different types of technical procedures and infrastructures.
Also, during the fourth quarter of 2022, it is confirmed that the most frequently used strategy is associated with scams that use email or similar approaches to reach potential victims.
Phishing is the most common strategy, but other scam strategies are also recorded. In particular, this quarter saw a significant increase in reports of smishing events, i.e. phishing attacks carried out via mobile messaging platforms, including non-SMS channels such as data-based mobile messaging apps.
The attribution rates are significantly better than for threat actors, even if still fairly low. Attribution means that it was possible to identify the external transfer pathway for a given event.
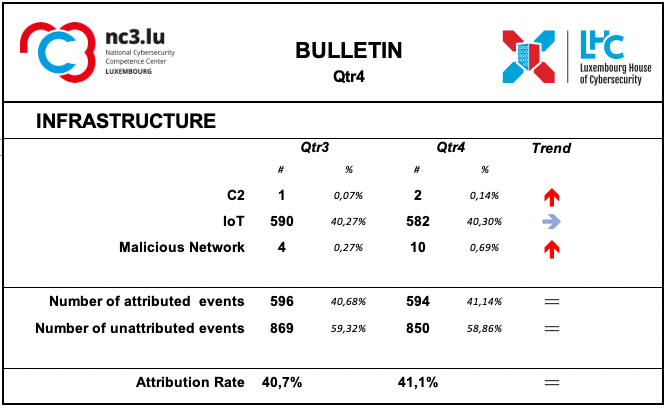
Infrastructures represent the type of systems being used for supporting attacks. Some are meant to compromise or help compromise, the targeted system, others are more focused on helping to maintain the foothold in it. Indeed, once access to a system device has been gained, a communication channel is maintained through the use of command and control (C2) infrastructures.
During this period, there has been a substantial confirmation of the number of events using Internet of Things (IoT) networks, which are equipped with sensors, software and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems via the Internet.
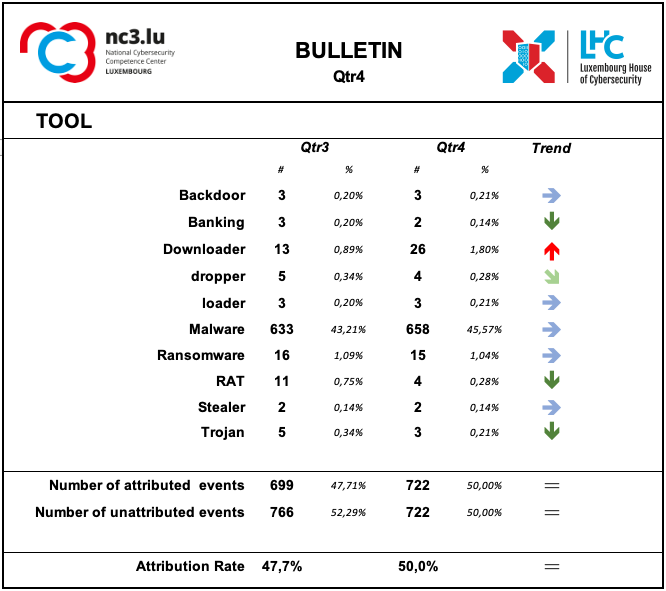
Tool
The monitoring system showed a substantial prevalence of the use of Malware especially associated with IoT systems.
The use of Ransomware tool is confirmed in the fourth quarter.
The use of downloader increased during this quarter. Downloaders are programs designed to fetch and install malware avoiding detections, without raising any security alarms.
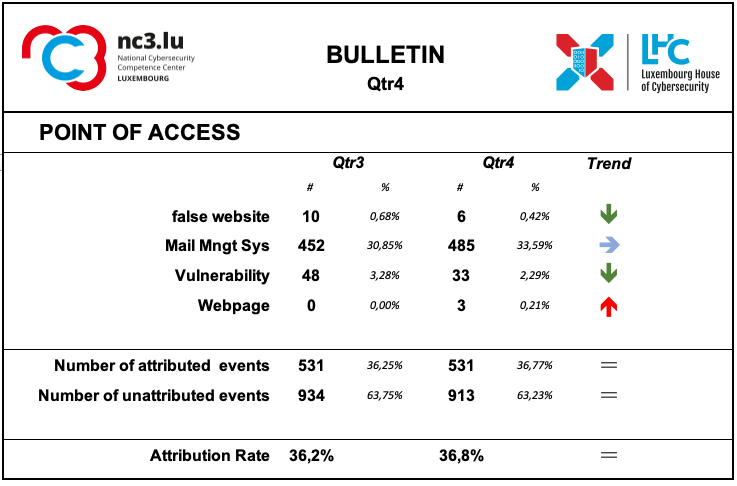
Points of access
The most common access point reported by MISP users is e-mail management system, which isn’t too surprising as it’s an effective ingress vector for several types of attacks. It’s often exploiting users’ weaknesses, be they voluntary (negligence) or involuntary (lack of knowledge about a specific threat.
The attribution rate did not change significantly during this period.
With regard to component and system vulnerabilities, the monitoring system identified the following:
Exploitation of CVE-2019-15859 allows the password disclosure in the web interface on socomec DIRIS A-40 devices and allows a remote attacker to get full access to a device;
NETGEAR ProSAFE Plus - Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution CVE-2020-26919 Scanner
D-Link DSL-2750BA - a remote attacker may be able to exploit this to execute arbitrary commands within the context of the application, via a crafted HTTP request (CVE-2016-20017).
D-Link Routers Information Disclosure Vulnerability – multiple CVE
Sonatype Nexus Repository Manager – multiple CVE
Netgear ProSAFE Plus networking switches – multiple CVE;
Kentico CMS Remote Code Execution Vulnerability – multiple CVE;
Artica Web Proxy allows remote attacker to bypass privilege detection and gain web backend administrator privileges through SQL injection of the apikey parameter in fw.login.php. (CVE-2020-17506);
SAP NetWeaver AS JAVA (LM Configuration Wizard), versions - 7.30, 7.31, 7.40, 7.50, does not perform an authentication check which allows an attacker without prior authentication to execute configuration tasks to perform critical actions against the SAP Java system, including the ability to create an administrative user, and therefore compromising Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability of the system, leading to Missing Authentication Check (CVE-2020-6287);
GLPI - manage Helpdesk and IT asset management software - a SQL Injection (CVE-2022-35947), and a Remote Code Execution (CVE-2022-35914, vulnerability in the third-party library, htmlawed), the latter has been massively exploited since October 3, 2022 to execute code on insecure servers, available on the internet, hosting GLPI;
Nette is a PHP/Composer MVC Framework - Nette is vulnerable to a code injection attack by passing specially formed parameters to URL that may possibly leading to RCE (CVE-2020-15227);
Linear eMerge E3-Series is an access control platform – multiple CVE;
HPE Integrated Lights-Out 4 - a authentication bypass and execution of code vulnerability in HPE Integrated Lights-out 4 (iLO 4) (CVE-2017-12542);
Certain WSO2 products (technology for cloud management) allow unrestricted file upload with resultant remote code execution (CVE-2022-29464);
Mida eFramework - there is an OS Command Injection that allows an attacker to achieve Remote Code Execution (RCE) with administrative (root) privileges. (CVE-2020-15920);
TerraMaster TOS - The vulnerability is due to insufficient sanitizing of user supplied inputs. A remote attacker may be able to exploit this to execute arbitrary commands within the context of the application, via a crafted HTTP request (CVE-2020-28188; CVE-2020-35665);
BeyondTrust Secure Remote Access Base Software - a cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability has been reported and confirmed for which allows the injection of unauthenticated, specially-crafted web requests without proper sanitization (CVE-2021-31589);
Linksys Devices - Remote Code Execution Vulnerability multiple CVE;
Atlassian Confluence Server - OGNL Injection Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability allows an unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code (CVE-2022-26134);
Inspur ClusterEngine V4.0. - A remote attacker can send a malicious login packet to the control server (CVE-2020-21224);
Sophos Firewall - an authentication bypass vulnerability allowing remote code execution was discovered in the User Portal and Webadmin of Sophos Firewall (CVE-2022-1040);
Mongo-Express is a Web-based Management Tool for administering MongoDB Databases interactively. It is vulnerable to the Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2019-10758);
OEM Presentation Platform – multiple CVE;
InfiniteWP Client plugin allows users to manage unlimited number of WordPress sites from their own server. An authentication bypass vulnerability can be exploited;
rConfig is a network configuration management tool – multiple CVE;
Web Console in Comodo UTM Firewall allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code without authentication via a crafted URL.
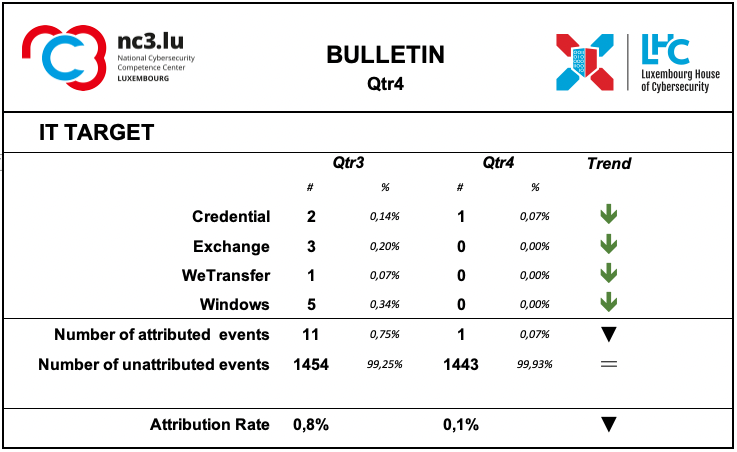
IT Target
Information on the attacked IT target is not sufficiently described by the analysed events.
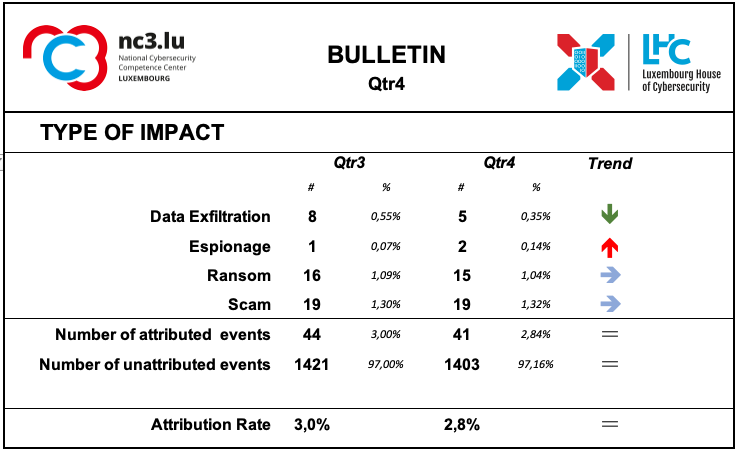
Type of Impact
The information detected by the monitoring system regarding the type of consequences for the victim is mainly related to ransom and scam demands.
The attribution rate of this class remains rather low.
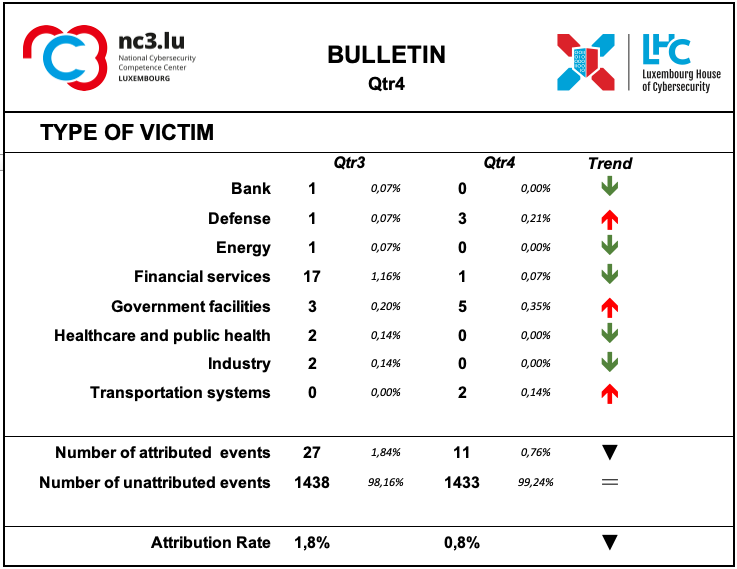
Type of Victim
During this quarter, there was a decrease in the number of events describing the type of victims affected and in absolute terms the number remains rather modest. Financial services showed a significant decrease in reports.