Network Segmentation
In Brief
Segmenting your network is a useful exercise that not only noticeably improves the security of your infrastructure, but also requires carrying out an inventory, which can be highly useful, and classifying your computer fleet. Segmentation consists of separating groups of computers into subsections, separated from one another by the use of well-defined rules.
If segmentation is done well, it does not just contain potential threats in predetermined areas, it also provides additional security tools.
Red Zone – Internet
Nowadays, the idea of a company IT system that is not connected to the Internet is unthinkable. The red zone is a zone over which we have no control, and this is where most threats come from. This zone should be separated from the rest of the internal network by a firewall or, at the very least, by a NAT router (as is the case for most households in Luxembourg). As a firewall is a computer that acts as a filter for communications between the zones, the filtering rules must be defined by the firewall’s operator but, generally speaking, connections initiated on the Internet will at least be blocked.
Only the services exposed directly to the Internet must be identified and isolated in the orange zone.
Orange Zone – Services Exposed to the Internet
The orange zone is the zone in which the company’s servers that are connected directly to the Internet can be found. Access to this zone must be carefully filtered (with the help of a firewall) to ensure that only services intended for external access are accessible; maintenance services should be protected against direct access from the red zone. No communication established in this zone must be able to enter another zone of the internal network.
Security can be improved with the help of switches that isolate the ports; doing so isolates all the servers from one another, containing the attacks if one server is compromised.
Green Zone – Staff Computers
The green zone is the core of the internal network. This is the zone with the most access, primarily to the Internet, but also with restricted access to the orange zone for server maintenance. In the green zone, it can be useful to have the machines talk to one another so isolating them is not always desirable.
Often, page filtering and virus detection web proxies are advantageously installed to reduce the risk of danger from the Internet.
The green zone can itself be divided into subsections. For example, IT team members are the only ones authorised to perform server maintenance in the orange zone. Therefore, they should be the only ones to have access to the maintenance services for these servers.
Warning! Do not be deceived by the colour: many attacks can originate from the green zone (dissatisfied employees, external threats that infiltrate the company or infected computers to name just a few); as a result, computers in this area should not be granted full rights.
Yellow Zone – Internal Services
You should pay particular attention to file servers, intranet server or other services intended for users in the green zone. The aim is to protect them against threats from the green zone while providing the access necessary for these services to be useful. This study must be carried out on a case-by-case basis. Nevertheless, this zone may be assimilated into an orange zone that provides services in the green zone instead of the red zone.
Installing the servers directly in the green zone might be more convenient, but should be avoided due to any possible dangers that might arise.
Blue Zone – Nomads and Visitors
The blue zone gives restricted access (often to the Internet only) to visitors or the staff’s private devices (iPads or telephones). This is typically the Wi-Fi area. Internal services should only be accessible from this zone by taking certain precautions.
Practical
Effective segmentation of the network can only be done using the appropriate tools. Firewalls, switches and, if necessary, Wi-Fi antennas make up the heart of a segmented network, through which it should be possible to get good results even at low cost using free products. Network segmentation is within everyone’s grasp and is very practical for small businesses.
Comments
As mentioned above, it is important not to consider the green zone a safe zone since this is where a large number of attacks can come from. The balance between ensuring the availability of services and security can be difficult to find, which is why it cannot be properly assessed without prior risk analysis.
Proper segmentation of the network does not offer total protection and should never be considered as such. You should instead think of it as a necessary tool for the introduction of other security measures, such as intrusion detection systems, filters, antiviruses, etc.
Examples
Small Network
Case of a very small business. Segmentation can be limited to the use of a NAT router to separate the internal Internet network.
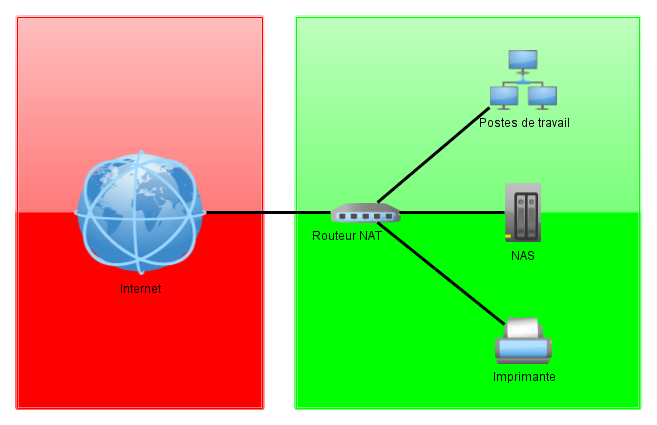
Medium-Sized Network
Case of a medium-sized company with a file and email server. A single firewall should take care of the network segmentation.
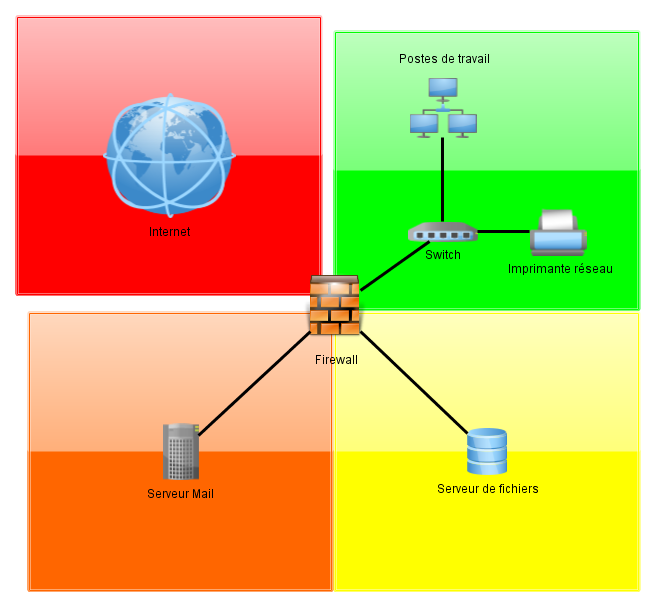
Large-Scale Network
Case of a large company with an external network and an isolated DMZ sub-network (orange zone in which the servers are unable to communicate with one another).

